In the June 1985 issue of Compute! magazine, in an otherwise innocuous editorial about font sizes and page layouts and column lengths, Richard Mansfield casually dropped a bombshell: that the number of companies in the PC industry had shrunk by 80% over the past year. Now, the reality was not quite so apocalyptic as that number (not to mention lots of fevered pundits) would make it seem. Many of the people and companies included within it were doubtless dabblers, who saw a chance to jump on a hot new trend, then saw the money wasn’t going to come so easily after all and walked away again. But still… 80%. Let’s look at some more numbers to try to unpack what that figure means.
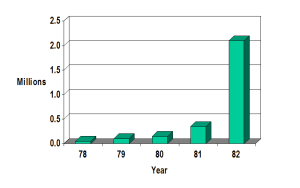
The chart above shows the numbers of actively used computers in American homes between 1978 and 1982. The first big spike came in the latter year, when cheap machines like the Commodore VIC-20, the Texas Instruments 99/4A, and the Timex Sinclair came online in a big way just as the videogame console market began to go soft. Home computers, the pundits said, were the logical successors to that fad, and consumers seemed to agree by almost quintupling their numbers in the space of a single year.
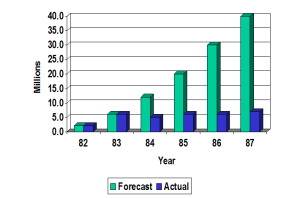
The chart above shows the actual and forecasted installed base of active home-computer users between 1982 and 1987. As you can see, things continued to go swimmingly through 1983 — the peak of the home-computer wars, Jack Tramiel and Commodore’s year of triumph. By year’s end, following the most spectacular Christmas of the 1980s for the home-computer industry, the number of computers in American homes was over 250% of what it had been at the beginning of the year. With millions upon millions of American homes still unconverted, everyone assumed that this was only the beginning of the beginning, that growth by leaps and bounds was inevitable until the end of the decade at least.
Things didn’t work out that way. Not only did 1984 fall short of projections by more than 50%, but sales to first-time buyers weren’t even sufficient to make up for those who got bored with their balky toys from the previous year or two and relegated them to closets, first step on their long, gradual journeys to the dumpster. (One research firm would later estimate that consumers threw out 1.5 million home computers in 1985 alone.) I’ve talked in earlier articles about the many perfectly good, sensible reasons that consumers grew so quickly disillusioned with their purchases, a list which includes a complete lack of killer apps — beyond games, that is — for the average household, the pain of actually using these primitive machines, and hidden costs in the form of all of the extra hardware and software needed to do much of anything with one of them. Home computers just didn’t live up to the hype; at least the old Atari VCS really was cheap and simple and fun, exactly as advertised. Most Americans found home computers to be none of these things. Their experience of 1982 and 1983 was bad enough to sour many of them on computers for a decade or more.
As bad as the chart above looks, it took a surprising amount of time for the industry to realize just how far off-track things had gone. 1984 was a paradoxical year of mixed messages in many respects, one that saw for instance the Apple II and Infocom both enjoy their biggest sales years ever. It wasn’t until 1984 became 1985, and the industry counted its dollars and woke up to the realization that the Christmas just past had been a deeply disappointing one, that the full scale of the problems set in and the dying-home-computer-industry became as big a media meme as the home-computer-as-social-revolution had been just a year or two before.
Still, some knew long before that something was very, very wrong. The bellwether of virtually any consumer-facing industry has always been — prior, at least, to the Internet age — its magazines. A healthy, growing industry means lots of readers buying at newsstands and signing up for subscriptions, as well as lots of vigorous new companies eager to advertise, to tell the public about all the new stuff they have to sell them. Conversely, when interest and sales begin to flag the newsstands start to reduce their magazine selection to make more room for other subjects, subscriptions are allowed to lapse, and advertising budgets are the quickest and least immediately painful things to cut. And as the first companies start to fold, those with whom they’ve signed advertising contracts tend to be about the last creditors to get paid. Woe betide the magazine that’s let itself go too far out on a limb — like, you know, one assuming it’s a part of an industry likely to grow almost exponentially for years to come — when that happens. The carnage in the magazines, those engines of excitement and advice and community, was appalling during the eighteen months between mid-1984 and the end of 1985.
The period was bookended by two particularly painful losses. Softalk, the de facto voice of the Apple II community, simply never appeared again after an apparently business-as-usual August 1984 issue. An even sadder loss was that of Creative Computing, which at least got to say goodbye in a last editorial (“Great While It Lasted”) in its last issue in December of 1985. The first newsstand magazine devoted to personal and, well, creative computing, it had been founded by David Ahl, a visionary if ever there was one, in October of 1974, months before the Altair. Ahl sold the magazine to the big conglomerate Ziff-Davis in 1982, but remained on as editor-in-chief right through to that last editorial. Throughout its run Creative Computing remained relentlessly idealistic about the potential for personal computing, always thinking about next year and of what the products they reviewed meant in the context of the ongoing PC revolution as a whole. Just to take one example: in response to the arrival of the first prototype laser-disc players in 1976, the magazine laid out a manifesto for what would come to be known as multimedia computing well over ten years later.
Creative Computing also published books, the best selling, most important, and most beloved of which was titled simply BASIC Computer Games, a compendium of type-in listings featuring games that had been making the rounds of The People’s Computer Company and the pages of Creative Computing itself for years. BASIC Computer Games sold a staggering one-million copies in English and in translations to French and German, years before any pre-packaged computer game would come close to such a feat. Many a young hacker pecked out its listings and then started to experiment by changing a variable here or a statement there, learning in the process the wonderful quality that separates computers from game consoles and just about every other form of electronic entertainment: that you can use the same device you play games on to also make games, or just about anything else you want. Creative computing indeed. The voice of Ahl, every bit as much a pioneer as a Steve Wozniak or Steve Jobs, would be sorely missed in the years to come. Ironically, his magazine’s end came just as machines like the Macintosh and Amiga were arriving to begin to bring to fruition some of his more expansive predictions of earlier years. (One of Creative Computing‘s last issues featured a gushing review of the Amiga which called it nothing less than “a new medium of expression.”) It’s a sign of the immense respect with which Ahl and his magazine were still viewed in the industry that several competing magazines took the time to remark the loss of Creative Computing and offer a warm eulogy — an act of graciousness unusual indeed in the increasingly cutthroat world of computer publishing. As Info magazine noted, “There could be no better history of personal computing than a complete collection of Creatives.”
In 1985 the pain spread in earnest to the software industry. Many pioneering companies, including some we’ve met in earlier articles on this blog, collapsed during the year. Any company that hadn’t shed its old crufty hacker’s skin and learned to start behaving like professionals was doomed, as were many who had listened a bit too much to the professionals and pundits and over-expanded and over-borrowed in the expectation of the perpetually-exploding industry that had been promised them. Also doomed was anyone whose creations just weren’t good enough; those users who had chosen to stick with this computer thing were far savvier and more demanding than the neophytes of earlier years. Muse Software of Castle Wolfenstein fame was amongst the victims, as was our more recent acquaintance Synapse Software, who were shuttered by Brøderbund barely a year after they acquired them. The Carlstons may have been nice folks, but their company didn’t survive by throwing good money after bad, and neither of Synapse’s principal assets — their expertise with the fading Atari 8-bit line and their Electronic Novel line — were worth much of anything in the evolving industry order.
Indeed, adventure-game makers were if anything hit even harder than the rest of the industry. By mid-1985 it was becoming clear that bookware had been a blind alley; virtually nothing in the category, excepting only Infocom’s The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy, did much of anything commercially. Companies like Spinnaker (owner of the Telarium and Windham Classics brands) and Brøderbund now began to divest themselves of their bookware assets almost as eagerly as they had acquired them. So much for the dream of a new interactive literature. Other expectations were also dramatically tempered. Trip Hawkins, for instance, was finally forced to give up on his dream of game designers as the rock stars of the 1980s and a shelf of games joining a shelf of records inside every hip living room. Electronic Arts now retrenched and refocused on becoming a big, highly respected fish in the relatively tiny pond of hardcore gaming (the only kind of gaming there was in this window between the Atari VCS’s collapse and the arrival of Nintendo). Yes, computer games were just computer games again.
Almost unremarked amidst all of the bankruptcies and retractions and cancellations was the collapse of Scott Adams’s Adventure International, one of the oldest of all the companies we’ve met on this site. Whether due to stubbornness or lack of funds or failure of vision or simple loyalty to what had brung’em, Adams had refused for years to upgrade his core technology, continuing to sell the same little 16 K, two-word-parser games he had started writing back in 1978. Their revamp into the SAGA line added crude graphics to the equation, but little else. Thus Infocom had long since stolen Adams’s crown as the king of adventure-gaming, not so much by besting him as by Adams not even trying to compete. Adams instead fed — and, for a time, quite well — on the ultra-low-end market, those machines like the Commodore VIC-20 and Texas Instruments 99/4A that weren’t a whole lot more capable than the original TRS-80 on which he’d first written Adventureland. These machines, unfortunately, were exactly the ones which found their way into closets and attics with the most frequency after the home-computer boom passed its heyday. Therein lay the root of AI’s troubles.
By 1984 much or most of Adventure International’s revenue was coming from Britain, thus belatedly justifying the company’s name, chosen in a fit of optimism when Adams and his wife were still making packaging out of baby-bottle liners and struggling to grasp the vagaries of wholesale pricing; expansion across an ocean must have seemed far-fetched indeed at that time. With their more modest cassette-based computers, their absolute mania for adventures, and their accompanying willingness to forgive faults and limitations Americans no longer were, Britons offered Adams a more hospitable market all around. An independent quasi-subsidiary, Adventure International UK, offered not just the classic dozen original Scott Adams games and the OtherVentures titles, but also many more games written in Britain by British authors like the prolific Brian Howarth using Adams’s engine. Adams himself was a celebrity amongst British adventurers. Everyone knew him for his crazy Afro that made him easy to spot across a crowded trade-show floor, and the magazines jostled for quotes and interviews and the fans for autographs whenever he made one of his occasional trips across the pond.
In late 1983 or early 1984 a tremendous opportunity to improve Adventure International’s standing on both continents virtually fell into Adams’s lap. Joe Calamari, an executive vice president with Marvel Comics, called Adams out of the blue to propose that Marvel and AI collaborate on a line of games and accompanying comic books starring the Marvel superheroes. While it would take many years for Marvel to catch up to their perpetual arch-rivals DC Comics in bringing their brand to the masses via the multiplexes, Marvel at this time was making a modest but in its way innovative push into trans-media storytelling via deals like this one and the one they inked around the same time with TSR of Dungeons and Dragons fame to do a Marvel tabletop RPG. Their choice of Adventure International for the computer-game license could be read as surprising; AI was hardly at the cutting edge of the game industry, and given the huge demographic overlap between gamers and comics readers the Marvel license would certainly have been appealing to other, slicker publishers. Perhaps AI’s support for the cheap low-end machines, not to mention their games’ typical price of $12 or so as opposed to $30 or more, led Marvel to consider them a better fit for their generally younger readers. (As with science fiction, the golden age for superheroes is about twelve.) As possible evidence of exactly this thought process, consider that Commodore, who may have suggested AI to Marvel and apparently did play some sort of intermediary role in the negotiations, had been doing very well with cartridge versions of the first five Scott Adams adventures on the VIC-20 throughout the peak years of the home-computer boom.
It’s hard not to compare this early, crude experiment in trans-media storytelling with the Marvel of today, whose characters feature in cinematic extravaganzas costing hundreds of millions to produce. We’ve certainly come a long way. (Whether it’s a change for the better is of course in the eye of the beholder.) It’s also yet another sign of just how huge text adventures were for a few years there that Marvel chose this format for the games at all. The cerebral pleasures of text and puzzles hardly feel like an obvious fit for the “Wham! Bam! Pow!” action of a superhero comic — not that this marks the strangest mismatch between form and content of the bookware era.
Adams signed a deal to make a dozen games with Marvel, one that gave him a crazy amount of creative freedom. He gave the series its truly awful name, the uncomfortably medicinal-sounding QuestProbe. (It’s choices like this that distinguish companies like AI, who couldn’t afford PR firms and image advisers or just couldn’t be bothered, from companies like Infocom who could. As for Marvel, who knows what they were thinking…) He also got a pleasure that would turn any superhero-loving kid — and more than a few superhero-loving adults — a Hulk-like green with envy: he outlined a story to accompany each game, then gave it to Marvel to be turned into a full-blown comic book to be sold as part of a “Scott Adams/Marvel Comics Limited Series.”
Alas, the Marvel deal, AI’s last, best chance to live and possibly even prosper, turned into an opportunity squandered. The QuestProbe games are painfully, shamefully bad by just about every criterion. The graphics are crude and ugly, the prose strangled, the situations all but incomprehensible (especially if you aren’t lucky enough to have the accompanying comic to hand), and the puzzles a hopeless mix of the inane and the inscrutable. They are, in other words, pretty much like all the other Scott Adams games after the first half-dozen or so, and that just wasn’t good enough anymore, even for the patience of twelve-year-olds. After the first game, which featured the Hulk, was roundly panned even by the forgiving gaming press (the making of a game bad enough to achieve that was something of a feat in itself), Adams did begin to include some modest innovations: the next game, featuring Spider-Man, debuted at last a parser capable of understanding more than two words (not that it was otherwise up to much); and the third and as it turned out final game, featuring the Human Torch and the Thing, had you controlling both characters, able to switch between them at will — an interesting idea badly executed. By the time that third game trickled out in mid-1985, AI was already collapsing.
Adams today notes the immediate cause of AI’s failure, no doubt accurately, as a rash of returned product from distributors who had over-ordered in anticipation of a big Christmas rush that never materialized. AI, which had never attracted the injections of venture capital and the accompanying professional financial oversight of fellow pioneers like Sierra, found themselves unable to pay back their distributors. With no one willing to extend them credit given conditions in the industry as a whole, there was no viable recourse but bankruptcy. Yet the deeper cause was Adams’s inability or unwillingness to change his games with the times. He’s stated many times in interviews that he virtually never looked at any of the games produced by his rivals; for instance, he never played an Infocom game after Zork. His logic was that he didn’t want to have his designs “polluted” by ideas and puzzles of others. This is, at best, an odd stance to take; try to imagine a novelist who refuses to read books, or a musician who doesn’t listen to music. It perhaps does much to explain the time-warp quality of the QuestProbe games. It’s strange that the man who had the vision and the technical chops to get viable adventures working on 16 K microcomputers in the first place should prove so unable to further iterate on that first masterful leap, but there you have it. Adams went on with his professional life as a programmer outside of the games industry, and Adventure International passed quietly into history.
One part of the brief-lived AI empire did survive. Mike Woodroffe, head of the still-viable Adventure International UK, disentangled that organization from its erstwhile namesake and renamed it Adventure Soft. The company would go on to a long if only sporadically active life as a developer of graphic adventures, whose biggest games became the Simon the Sorcerer series, The Feeble Files, and two Elvira-themed pseudo-CRPGs. Adventure Soft continues as an at least nominally going concern today, although their website is little more than a storefront for sometimes decades-old titles.
All told, then, 1985 was a brutal year in American software and particularly games software, one that weeded out the weak sisters like Adventure International, Muse, Synapse, and countless others without remorse — not to mention the casualties in publishing and hardware and still other, ancillary areas. Old timers who had grown up as hackers with many of the year’s casualties can be forgiven for seeing it in terms as apocalyptic as did the more hyperbole-prone members of the media. David Ahl, from his final Creative Computing editorial:
The personal-computing industry is largely composed of adolescent companies and inexperienced managers being forced to grow up much too fast by market forces that they themselves created. The big guys are sailing in with battleships, and the friendly competition of a few years ago has become all-out war with no holds barred. The media smells blood and death, which makes for interesting reading (and sales). Their alarmist disaster stories have simply exacerbated the situation.
Still, if we’re seeking silver linings they aren’t that hard to come by. Just to take the obvious: another look at the chart above will show that, if the home-computer user base wasn’t growing much, it also — that one brief blip in 1984 aside — wasn’t shrinking either. There was still a very viable, even vibrant market there. It was just a market that had reached an equilibrium far, far sooner than anyone had anticipated. The pain of 1985 was the pain of adjusting expectations to match that reality — the reality that numbers of computers in homes wouldn’t increase in big jumps again until the arrival of the Internet and cheap multimedia PCs in the early 1990s gave everyone a good reason to own one. The generation of microcomputers sandwiched between those and the old 8-bits — the Apple Macintosh, the Atari ST, the Commodore Amiga, the Tandy 1000 and a rash of other ever cheaper and more capable MS-DOS-based machines — would seldom be sold to complete neophytes. They would rather go to people looking to upgrade their old Apple IIs, Commodore 64s, Atari 800s, and TRS-80s. A tempering of expectations, especially for hardware makers, would be necessary. Not everyone would upgrade, after all, meaning home-computer sales wouldn’t come close to their 1983 peak for many years to come. As David Thornburg noted in a perceptive article for Compute! magazine, computers were and would for years remain a hobby, not an everyday home appliance.
If you go to someone’s house and see a computer sitting in the den, I’ll bet you say, “Hey, I see you’re into computers. How about that!”
Have you ever gone into someone’s house and said, “Hey! I see you’re into refrigerators. Wow! Automatic ice-cube maker too! I was going to get one of those myself — thought I’d get a 16-cube model, but then I heard that the 32-cubers were going to come out soon.”
If the home computer was an appliance, we would talk about it like one.
David Ahl offered another comparison to explain why the home computer hadn’t yet achieved appliance status and wasn’t likely to for some time to come.
People who don’t have computers are looking for user friendliness of a sort that just isn’t available today. You can rent a car virtually anywhere in the world and in a minute or two be familiar enough with the vehicle and local traffic laws to drive off with a reasonable degree of confidence. When it is that easy to use a computer, then manufacturers can legitimately speak of user friendliness. We are a long way from that point today.
When a reeling software industry proved unable to fill the space allocated for it at the 1985 Summer Consumer Electronics Show, a big chunk was instead given over to pornographic videos, an industry that was thriving on the back of booming VCR sales in exactly the way the software industry wasn’t on lukewarm home-computer sales. Game consoles and home computers may come and go, but some interests are eternal.
If you were a committed gamer in for the long haul, however, the outcome of all this chaos was arguably at least as positive as it was negative. With computer owners an ever savvier and more experienced lot unwilling to suffer bad or even mediocre games anymore, with publishers all competing frantically for a big enough slice of a fixed pie to keep them alive, games in general just kept getting better at a prodigious rate. By 1986 developers would be taking the Commodore 64 in particular to places that would have been simply unimaginable when the machine debuted back in 1982. And as for the next-generation machines… well, even more splendid work was in the offing there. Everything was improving: not just graphics and sound but also the craft of design.
But before we can revel too much in the positives we have more pain to address. Next time we’ll look at Infocom’s disastrous 1985, the year that came within a whisker of cutting off the most beloved canon in interactive fiction at the halfway mark.
(My huge thanks to C. David Seuss, former CEO of Spinnaker Software, who answered my questions about this era, pointed me to a useful Harvard Business School Case Study, and provided the charts shown above and other documents. The usual thanks also to Jason Scott, whose interview with Scott Adams for Get Lamp was also invaluable. Useful magazine sources this time included: Compute! of March 1985, June 1985, and January 1986; Your Computer of November 1985; Creative Computing of December 1985; Computer Gaming World of January 1985; Computer and Video Games of May 1986; Info of December 1985/January 1986. Finally, if you don’t believe me that the QuestProbe games are really, really bad, feel free to download them in their Commodore 64 incarnations and see for yourself.)

















Andrew Plotkin
March 28, 2014 at 9:27 pm
“Their experience of 1982 and 1983 was bad enough to sorrow many of them on computers for a decade or more.” …I bet you meant “sour”.
“There could be no better history of personal computing than a complete collection of Creatives.” …which, of course, we can now all share: https://archive.org/details/creativecomputing
What’s weird is that the industry crash, like the videogame crash of a couple years earlier, was practically invisible to me as a teenager. I have an excuse re 1983 — I never had an Atari device and I wasn’t paying that much attention to arcades.
But for computers in 1984-5… well, I remember a couple of magazines disappearing, but the notion that *home computers* were in any sense disappointing people never crossed my radar. Shows you how obsessed a teenager can be, I guess.
(In contrast, I remember being *very* nervous about Infocom’s acquisition. “What can Activision do with them?” I asked my father. “Anything they want,” he said.)
Jimmy Maher
March 28, 2014 at 9:43 pm
Yep, thanks.
I was the same way. I saw the articles in the magazines saying that the industry was having problems and that Commodore (I had a 64) wasn’t doing all that well, but I can’t say I ever saw them as any sort of existential threat. My local Babbage’s still had tons of shiny games on the shelf that I desperately wanted — more than ever in fact. (Whatever else you can say about the crash, it didn’t keep games from continuing to get better and better.) Nor did I ever really think much about where the games came from or the idea that people needed them to make money. They were just all these amazing worlds I wanted to play in, which might as well have dropped out of heaven. Kind of a beautiful innocence really, not knowing how the sausages are made.
I don’t think I had my first inkling that Infocom might not be around forever until even after you, when the packaging suddenly got noticeably cheaper in 1987.
Atari Mike
March 31, 2014 at 9:46 pm
I certainly noticed it. IBM and later Apple with the Macintosh was sucking all the oxygen out of the room. Computer stores were either closing or becoming IBM PC shops. The shelf space for 8 bit books at bookstores and libraries were dwindling. 8 bit computer magazines were getting thinner or disappearing, and general computing magazines started focusing on “business computing” instead. Even old Creative Computing was not immune. It stunk. I felt the whole home computer movement fading away with overpriced, often limited (in the case of the PC) machines with the only option left–a choice few of us could afford. IBM was overpriced and the machines really stunk for anything interesting. The apple Mac was cool, but no home could realistically afford one.The Amigas and Atari ST’s were great machines that could have filled the home computer void, but they cost 3-4 times as much as the old 8-bits and priced themselves out of the home, too. The decline was definitely noticeable. By 1985, the entire microcomputer ecosystem had all but vanished, Commodore and Atari along with them. No one was left. :-(
Sniffnoy
March 28, 2014 at 9:41 pm
Sorry, just some typo-pointing-out: In “shamefully bad by just about every criteria”, “criteria” should be “criterion”.
Jimmy Maher
March 28, 2014 at 9:50 pm
Thanks!
Keith Palmer
March 28, 2014 at 10:43 pm
Remembering your post “A Computer For Every Home?”, I saw this post as an expansion of some ideas introduced in it. The pause in the growth of computer ownership in the home never quite registered on me until you pointed it out (after all, we had our own computer in the home at the time), but now I can sort of see it as having its own effect on “where all the old platforms went.”
With the point briefly made in your previous post about some well-respected computer magazines folding in 1984 and 1985, I was surprised to see a full tribute to Creative Computing here, but quite glad too. When my family moved at the beginning of the 1990s, our old computer magazines turned up in the basement, including the last fourteen issues of Creative Computing (which our subscription had been transferred to after Ziff-Davis’s “The Color Computer Magazine” had folded). Around the same time, I found “The Best of Creative Computing volume 1” and assorted other issues in a classroom at high school, and found something about the magazine particularly appealing; that might have been where my whole interest in the topic of “old computers” comes from. I’ve seen a number of those period editorial notices on its passing you mention, but I’m afraid not all of them were full tributes; I keep remembering the comment from 80 Micro editor Eric Maloney in March 1986, who said “Creative Computing never appealed to me; it felt too much like a comic book.” However, in noticing Info’s warmer tribute I also noticed that magazine pointing out some months later that David Ahl and a few other people from his magazine had found work at the “house organ” Atari Explorer; their years there weren’t quite the same wide-angle view on the topic, but did still keep some of the old spirit.
Jimmy Maher
March 28, 2014 at 10:59 pm
I didn’t know Ahl wrote for Atari Explorer. He’s something of a hero of mine, so I’ll have to check it out.
I was moved to write more about Ahl and Creative Computing when an email inquirer mentioned him as just “the programmer” of an old BASIC game about which she was inquiring. I realized that was my fault for never fully explaining his role and legacy…
Keith Palmer
March 29, 2014 at 1:53 am
The chance to say more came not too late, anyway. I realised myself I forgot to mention being amused by the link to the Rambo text adventure, having seen it negatively reviewed in the back of another issue of 80 Micro; despite adding some coverage of Tandy’s MS-DOS systems in an increasingly uneasy blend with features for the remaining Tandy Z-80 system users, they hardly ever reviewed games by 1986. To say any more about that, though, I’ll have to wait and see if you mention Moonmist…
Steve McCrea
March 28, 2014 at 10:46 pm
Yeah, those QuestProbe games are shameful.
I don’t think you can rely so much on the forecast installed base graph since it’s just a single forecast without attribution. However I don’t doubt the general trend was the conventional wisdom…
Typo: causalities instead of casualties (2x).
Interesting article as usual, thanks!
Jimmy Maher
March 28, 2014 at 10:57 pm
Thanks!
These numbers are sourced from Spinnaker Software’s internal forecasts of the period. Being one of the more “professional,” VC-backed software firms of the period, I feel pretty confident that they represent the general industry’s best guess about where things were headed.
Wade
March 29, 2014 at 9:14 am
Same story for me as several folks above. I read some talk of the computer industry crash in Electronic Games magazine around 83, 84 (so I was 8-ish and flush with our Apple II) but didn’t notice or feel anything then or later, and I was too little to understand what these articles were talking about.
We had heaps of Creative Computings and both the Ahl Computer Games books. The latter two are on a shelf less than a metre behind my head as I type this. They helped me get going in programming games.
I was shocked when one day my dad bought a Creative Computing home after a bit of a gap, and it was this super slim thing that barely resembled the older ones. I guess that would have been nearer the magazine’s end. I remember it had a Dicky Tracy watch on the cover. I kept my favourite issues and I’ve still got them. If I’d been older when I did the cull and had more space, I expect I’d have kept them all.
Dehumanizer
March 31, 2014 at 8:27 pm
As always, a great read. Just a few thoughts:
– this is one of your longer posts, isn’t it? Don’t get me wrong, it’s a fascinating subject to me (computers + games + history + my own childhood memories) and a joy to read, but you talk about several relatively unrelated topics that could, perhaps, deserve separate posts (e.g. the QuestProbe games and the end of AI, the Creative Computing magazine, etc.).
– you seem a bit dismissive of superhero comics, another of my “loves”, as entertainment fit just for 12-year-olds (something people also often say about computer games, and we all know they’re wrong :) ), but maybe I’m reading too much into it. :)
– like others, I didn’t notice any kind of “crash” at the time, though, come to think of it, the many 8-bit computers common in 1983-4 (Oric, etc.) weren’t around anymore just a couple of years later. But then I lived (and live) in Portugal, and here the Spectrum and later the Amiga ruled the universe, until the rise of the multimedia PC in the early 90s.
– there was a Rambo text adventure? I hadn’t followed the link until I read the comments, as I thought it was about the Commando-like C64 / Spectrum action game, which wasn’t really that weird a match…
– the QuestProbe games had, IMO, decent graphics… in the Atari 800XL disk versions. The ones you show are from the Apple II, right? I remember them being even worse than these on the Spectrum, which was where I played them at the time.
Jimmy Maher
April 1, 2014 at 6:28 am
I’m fairly neutral on superheroes in general. I read them for a few years around the age of twelve, as it happened. :) But I was more repeating conventional wisdom in the article than trying to be dismissive. I will say that I hugely prefer the funkier, scruffier Marvel of the 1980s to the soulless Marvel films of today. But I’m really not qualified to say much more.
Funny story: shortly after my wife and I got together, my dad found and gave me a stack of comics from my aforementioned comics heyday. Dorte started reading them, and developed an addiction to Captain America — doubly strange because all the strident flag-waving is one of the things that drives her crazy about America. I spent quite some time scouring comics shops for more old Captain Americas. Later she graduated to Watchmen and other more modern graphic novels. So she’s really the comics expert and fan in our house…
Graphics shown above are from the Commodore 64 version of Human Torch and the Thing.
Eddie in Miss
April 2, 2014 at 10:28 pm
Hi Jimmy, there were only five Scott Adams cartridges created for the Vic-20, The Count being the last one.
Thank you for your excellent web site.
Jimmy Maher
April 3, 2014 at 7:34 am
Thanks, correction made.
David Boddie
April 3, 2014 at 8:37 pm
According to Merlin in his June 1986 edition of his column in Electron User, Adventure International UK ceased trading at around that time, though it seems it was only a trading name of Adventure Soft.
Alex Smith
January 1, 2017 at 7:18 am
Just happened to be browsing this today and noticed an error: BASIC Computer Games was first published in 1973, not 1978. At that time, it was aimed at the minicomputer and time-shared mainframe crowd rather then the non-existent micro market. A second printing occurred in 1975 before the 1978 printing explicitly targeted at microcomputer users.
Jimmy Maher
January 2, 2017 at 7:21 am
Thanks! Fixed via some judicious deletion.
Jason Kankiewicz
January 28, 2017 at 9:30 pm
Is “C. Davis Seuss” actually “C. David Seuss”?
Jimmy Maher
January 29, 2017 at 7:37 am
Thanks!
Ben
October 31, 2021 at 9:40 pm
bellweather -> bellwether
Jimmy Maher
November 2, 2021 at 4:14 pm
Thanks!