I’ll give you an analogy of what Populous is in my mind. Imagine if I had a blank canvas. Some people that are true artists will take a palette of paint and mix them together and carefully handcraft each and every single brushstroke until they have some beautiful and amazing picture. And then there’s me. I had the blank canvas, accidentally knocked a can of paint over, and it went splat. And an art dealer has seen it and said, “That’s brilliant.” Well, I know all I’ve done is kick a can of paint. And that’s what I believe really happened with Populous.
— Peter Molyneux
When we last met Peter Molyneux and his little database-developer-turned-games-studio Bullfrog Software, they had just made Populous and watched in disbelief as it blew up huge. The radically innovative game joined Will Wright’s SimCity as one of the progenitors of a hazily delineated new genre which the media labelled the “god game” for the way it gave you direct control over an environment but only indirect control over the people therein. As Populous became a hit on three continents and sold in the hundreds of thousands and eventually millions of copies, Bullfrog struggled to reckon with the cognitive dissonances of their changed circumstances. In a matter of months, they went from a handful of poverty-stricken dreamers pissing in the sink of their miserable, toilet-less hovel of an office to Britain’s single most successful and respected games studio of all.
The trappings of their success tended to trail behind their sales figures: when a group of Japanese executives stopped by the Bullfrog hole-in-the-wall to discuss plans for publishing Populous in their country, the senile pensioner who lived below met them at the bottom of the stairs with a mop and proceeded to beat them off the premises. “We had to get out of there as soon as possible,” says Molyneux. They wound up in a more conventional business park, whose more conventional tenants complained endlessly about their penchant for racing skateboards through the hallways and shooting BB guns out the windows. (“We were brats,” admits Molyneux today. “Horrible, horrible brats.”)
While certainly preferable to failure, success could be its own kind of mixed blessing. Expectations of Bullfrog, which had previously been nonexistent, were suddenly sky high. After a quickie add-on disk that brought additional levels and environments to Populous, they made a rather shockingly unambitious little platformer called Flood, a project of Bullfrog programmer Sean Cooper. Released only in Europe for the Commodore Amiga and Atari ST by Bullfrog’s publisher Electronic Arts, it garnered a collective shrug from the magazines; the market was already flooded with platformers much like this one, often with more compelling level designs. This sort of derivative work wasn’t at all what people had come to expect from Bullfrog after Populous.
Luckily, they had something else in the works. Released in late 1990, some eighteen months after Populous, the real-time war game Powermonger evinced a lot of innovation on its own terms even as it clearly drew from the same set of techniques and approaches that had yielded Bullfrog’s first hit. Instead of casting you as a god able to alter the very landscape of the world on behalf of your mortal followers, Powermonger cast you as an ordinary human on a mission to conquer the world — all 195 regional cross-sections of it, one region at a time. The ethos of indirect control that had made Populous so unique remained: you had to convince the people to rally to your cause, and had to work constantly to keep them loyal to you. Ditto a focus on large-scale environmental effects: you had to worry about the ecology of the land in order to feed, water, house, and equip your people. (After all, it’s hard to build much of anything if you’ve already clear-cut all of the forests…) While Computer Gaming World‘s Johnny L. Wilson, who was always eager to read meaning into games, may have been overstating the case when he called Powermonger “a dynamic treatise on the human capacity for aggrandizement and the potential consequences therein,” the same magazine’s description of it as the “thinking person’s Populous” was a good deal more tenable.
Unfortunately, it suffered from many of the same flaws as its predecessor — flaws which would become consistent hallmarks of Molyneux’s work in general. He obviously wanted to give players a lot of game by providing 195 levels, but, being all procedurally generated, they didn’t really build upon one another or force the player to reevaluate the tools at her disposal in interesting new ways. Powermonger was great fun at first — thus all the glowing reviews in the magazines — but it started to feel a little bit rote a little bit too quickly.

The graphics in Powermonger got a dramatic upgrade over those in Populous, yielding not only aesthetic but also practical benefits: it was now possible to rotate your view of the landscape and zoom it in and out as needed, while the variety of landscape features was dramatically greater. “In Populous,” noted Molyneux, “we had hills, houses, and rivers. Thanks to this new system, we’re able to generate waterfalls, cliffs, valleys, mountains, proper towns, road networks, forests… it’s a real world!”
Molyneux originally conceived of Powermonger not so much as a standalone game as an engine for running a variety of them. After the first game with its vaguely Medieval theme, he talked of making a World War I version, a high-fantasy version, an Asian version for the Japanese market, and a version focusing on the American Civil War for the punters in the United States. But Powermonger, while moderately successful, never became the sensation that Populous was, and most of those plans were abandoned; only the World War I data disk ever appeared. Powermonger “appeals to a lot of people who like very, very high strategic games, but it needed that extra element that would appeal to everybody and it didn’t have that,” said Molyneux after the dust had settled. He blamed the lack largely on the pressure Bullfrog was under from Electronic Arts to complete and release the game in time for Christmas, which meant that it didn’t get played prior to release to anywhere near the extent of Populous.
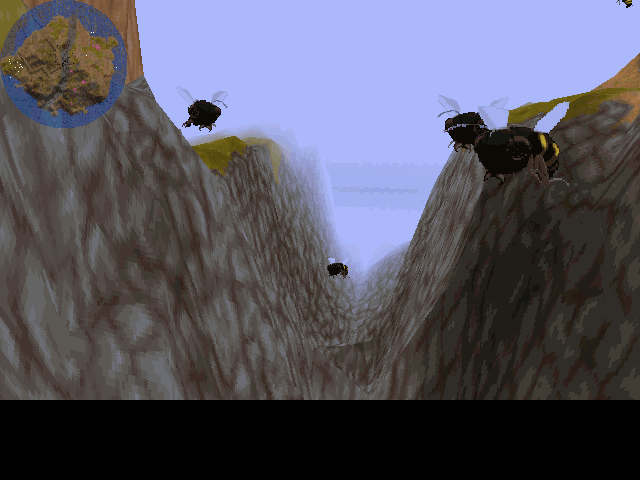
Still searching for that elusive second million-selling hit, Bullfrog opted to drink even deeper from the old Populous well next time around. Their game for the Christmas of 1991 was Populous II, which mated the improved interface and graphics of Powermonger to the literal god-game theme of Populous I. There was slightly more semblance of a plot this time out: you played a minor deity who must fight her way through a pantheon of some 35 Greek gods, culminating in Zeus himself. Your powers too were more varied than last time out; no longer could people scoff that the game was nothing more than an elaborate topography simulator, not with your ability to spawn tidal waves, whirlwinds, and lightning strikes. Yet one only had to glance at the screen, or read about its more than 1000 (!) anonymous, procedurally-generated levels to know that this was still very much Populous, for both good and bad. It sold well to the committed faithful and spawned the by-now standard expansion pack; in a sop to the Japanese market, where the first Populous had become so popular as to spawn graphic novels and symphony concerts recreating the game’s soundtrack, the expansion was set in ancient Japan rather than Greece. But even so, Populous II made relatively few new converts to the cause at home or abroad.

Populous II. Molyneux admits to feeling “ashamed” at the time to be doing a sequel at all, but he felt obligated to deliver a direct follow-up to such a massive hit. He considers Populous II a reasonable but somewhat unimaginative sequel, which in rather typical industry fashion added a lot more stuff to the template of its predecessor in the form of new godly powers, but failed to drill down on what actually made the original fun. A fair assessment, I think.
Although their latest games hadn’t sold quite as well as the original world-beating Populous, Bullfrog remained the preeminent British games studio in the minds of many. Their status was rivaled only by that of DMA Design, whose Lemmings had become upon its release in early 1991 the most successful single British game since Populous. But DMA was located way off in Dundee, Scotland, a country away from the press on Fleet Street, and when an intrepid journalist did make the trek out to those hinterlands its founder David Jones didn’t provide as many choice quotes as the gregarious Peter Molyneux, then as now one of his industry’s greatest raconteurs. The press loved him not least because he was so willing to go against the official industry position on many subjects, full speed ahead and damn the torpedoes. Asked about the effects of piracy — a subject guaranteed to produce predictions of an imminent gaming apocalypse from any other prominent industry figure — Molyneux shocked his interviewer by replying mildly that “to be honest, I don’t think that piracy hurts.” Likewise, he never hesitated to air his real feelings about competing products: “If you’ve got a crappy shoot’em-up style game, then that’s going to be pirated to hell — and it should be because it’s not even worth using this planet’s resources to produce the game.”
The chain-smoking, perpetually hyperactive Molyneux got on particularly splendidly with the laddish British Amiga magazines of the time. He was up for pretty much anything when they came calling — as when he agreed to be interviewed about a recent trip to Japan while sitting on the toilet. From here he regaled his interlocutors with anecdotes about geisha girls, and told them that “Peter Molyneux” meant “wooden tit” in Japanese: “If I wanted to break the ice anywhere I just said ‘Molyneux’ and the whole room would break up.” He cultivated the persona in such interviews of a slightly befuddled ordinary bloke who liked to spend his time down at the pub when he wasn’t making games, who had no idea how he had stumbled into this charmed career of his. Substitute playing games for making them, and remove the charmed career, and he seemed of a piece with most of the people reading the interviews. He never missed an opportunity to run down his programming skills. “When we wrote Populous,” he said, “we barely knew how to put a sprite onto the screen.” In the end, he claimed, “programming isn’t really that skillful. Anybody can learn to program, anybody, within a week.” Asked to describe Bullfrog in a single sentence, he did so in three words: “Disorganized but keen.” Or, as he put it on another occasion: “We write computer games. We’re not businessmen.”

The Peter Molyneux toilet interview for Zero magazine in December of 1991. Molyneux had by then perfected the art of press relations, which in the case of the gaming magazines often came down to the simple expedient of taking the youthful journalists down to the pub and getting them blind drunk.
In keeping with this everyman persona, Molyneux evinced no interest whatsoever in professional credentials. Recruitment at Bullfrog operated on the principle of “show us what you got,” via little classified advertisements placed in the nether reaches of the same magazines that were featuring Molyneux and his games on their covers. Bullfrog endeared themselves even more by running tutorials in said magazines, teaching graphics and programming tricks; at least one series of tutorials concluded with a contest for those who had been following along diligently, the prize a potential job with Bullfrog. “You too can make games!” was the message. And people loved Molyneux for it.
But there was also another side to Molyneux: the side that was a real businessman, whatever his claims to the contrary — a businessman who was watching his industry with eagle eyes. When someone deigned to ask him a serious question, he could deliver a cogent, sometimes even prescient response. For example, when asked whether personal computers would ultimately win out over consoles as game-playing devices, he had this to say:
Definitely not. PCs are too much bother, even with CDs. You’ve got to configure one of the 30 trillion sound cards’ 30 trillion settings. I don’t understand all these DMAs and IRQs and all that crap. I just fiddle around until I get it right. Until they sort that out, the machine is just going to terrify people.
About the general state of games in the early 1990s, he had this to say:
The current trend in games like simulations, adventures, and some sports sims is that they are getting progressively harder, cleverer, and more challenging. But that doesn’t necessarily make them better games. The trouble is that a lot of games are getting so hard that only the very best gamers can play them. The first rule of game design is that you mustn’t produce games that are too complex for people to play. Being overly complex for the sake of being complex is not a good idea. Complexity is good as long as it doesn’t get in the way of the game.
And this:
We’re into a new thing called interactive drama. Everybody’s doing interactive drama with interactive plots and interactive characters. But I think it’s going to be a tough, tough thing to do. Hollywood spends millions of pounds on scripts. They have hundreds and hundreds of scriptwriters and they get it right once or twice a year. And little game designers like us are coming along and we’re going to write this script which is going to have infinite variations, is going to be as entertaining as any Hollywood film, is going to have cinematic sequences in it, and we’re going to sell it for four times more than you can buy a video for. There’s something wrong there. Either we’re very, very clever chaps and Hollywood has been doing it wrong for the last 100 years, or perhaps we’re talking out of our arses.
Quotes like these made Molyneux into something of a spokesman for the British games industry, in the mainstream as well as the specialty press. Whatever the intrinsic merits of claims like those above, they had the advantage of poking holes in exactly the sorts of games which British studios tended to lack the resources to do as well as the Americans.
During this period, British games still largely meant Amiga games. Thus it was tough for Molyneux, both in his role as spokesman for his industry and as a proud Briton, to admit that Bullfrog just couldn’t continue to develop their games on the Amiga first and remain competitive in the international market; the latest MS-DOS machines were pulling too rapidly ahead of Commodore’s trusty old platform. Bullfrog’s next big project after Populous II would be developed first on MS-DOS and then ported to the Amiga in slightly downgraded form — the opposite of the studio’s earlier approach. For, as Molyneux put it, “you can let your imagination run wild” on an MS-DOS machine.
The same project would be a welcome, much-needed departure in both form and content from the games Bullfrog had spent the last few years making. It would be a much grittier, more down-to-earth affair of rival corporations doing battle with one another in an oligarchic worldwide dystopia of the near future. As such, it was of a piece with many of the print fictions which young men like the Bullfrog crew were reading in the early 1990s — think Neal Stephenson’s Snow Crash and, reaching just a little further back, William Gibson’s Neuromancer, the original popularizer of cyberpunk cool. (Self-effacing as ever, Molyneux claimed that “I read the first three chapters of Neuromancer, but it all went a bit above my head.”) Still, Bullfrog did add their own sprinkling of dark British humor to the mountain of cyberpunk clichés. For many months, they called the game simply Bob, after the infamously ruthless British media mogul Robert Maxwell, whose suspicious death aboard his luxury yacht and the subsequent revelation of financial malfeasance throughout his empire dominated tabloid headlines during the period.
In the end, though, Bob became known as Syndicate. Bullfrog spent a full two years working on it, marking the longest gap between games in their entire history as a studio. They claimed the end result to contain as much code and graphics as every one of their previous games combined.
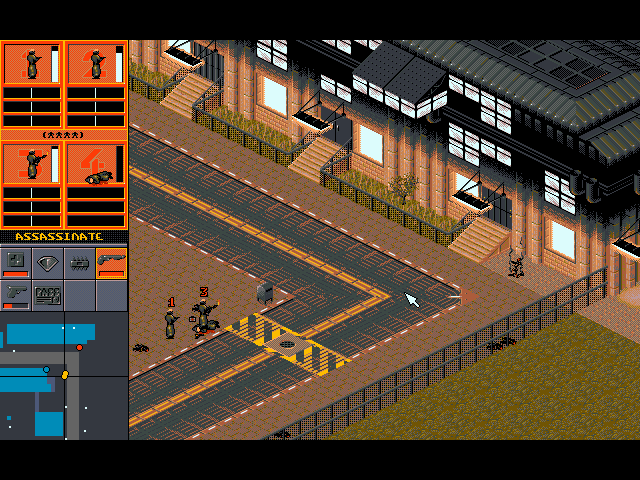
Whereas Populous and its descendants were played entirely from a single interface, Syndicate was a more disparate affair. As the owner of a tiny upstart corporation bent, naturally enough, on taking over the world, you had to allocate research funds for equipment and cybernetic enhancements for your army of operatives, whilst choosing missions to send them on from a Risk-like strategic map. But it was in the missions themselves, which played out in real time from an isometric perspective, that you spent the vast majority of your time. Here you had more direct control over your operatives than you did in Populous, but they still had minds of their own, which could cause them to react with a spontaneous burst of gunfire if, for example, an enemy agent popped up in their path; it might also cause them to refuse to obey an obviously dangerous command. The missions took place in living city streets replete with civilians as well as combatants, presenting ample opportunities for mayhem. Syndicate has been called a proto-Grand Theft Auto, what with the way it tempts its player to indulge in random violence and acts of destruction for their own sake.
Indeed, when it finally appeared in late 1993, just weeks before id Software’s landmark DOOM, Syndicate struck many as the natural British companion to that American game, another avatar of a movement toward ever more visceral forms of violence in games. As in DOOM, blood splashed everywhere in Syndicate with gleeful abandon, and much of the appeal of acquiring new weapons was in the visible carnage they created. This prompted a brief-lived round of nervous stock-taking in the magazines of both countries — until the same magazines, seeing that hordes of players loved the violence, learned to defer to the readers who buttered their bread.
Extreme though it was by contemporary standards, the violence in the finished Syndicate was reportedly toned down from earlier versions, where you had been allowed to kill babies and pets. Play testers “told us we were going too far,” mused Molyneux. “Funnily enough, they objected most to killing the puppies…” Yet he remained unapologetic on the whole:
We made Syndicate high in gore to be more realistic. I know this sounds like a cop-out, but it’s the player who’s violent, not us. All we’ve done is give a loaded weapon to the player and it’s up to them how to use it. I’ve always hated games that gloss over violence. Surely showing the realism of a violent act is better than disguising it? It’s not that Syndicate had done anything new with violence, it’s just that it shows it like it is.
For all the changes it evinced over what had come before, Syndicate was a typical Bullfrog game in other ways. It started out thoroughly entrancing, but went on way too long, with only a handful of fixed mission types on offer as you slowly — very slowly — took over the world. By the mid-game, you had discovered most of the cool gear and cybernetic enhancements, and what had started out fresh and exciting had begun to turn into a bit of a grind. Thus Syndicate became another Molyneux game that far more players started than finished. Nevertheless, its initial appeal was enough to make it Bullfrog’s biggest hit since the original Populous, and the game and its 1994 expansion pack are still fondly remembered by many today.
By this point, Bullfrog had grown from just a few employees to about forty, enough to have multiple projects on the boil at one time, all receiving varying degrees of attention from the hardworking and endlessly enthusiastic Peter Molyneux. Thus the next game arrived barely six months after Syndicate. It would prove to be one of Molyneux’s most influential creations of all.
The project had its genesis in the first game he ever made, a text-only business simulation called Entrepreneur, of which he had sold exactly two copies — one of them quite possibly to his mother — in 1983. That failure had continued to rankle even amidst all the success he enjoyed in later years, as did the urge to make another, less dry business simulation that would appeal to more people. “Then one day the perfect idea hit me,” Molyneux says. “I’d create a game where you control a theme park.” Molyneux:
I love theme parks, and it was a great excuse to do some really good research. It’s also something where you often go back and think, “If I’d been given the chance to design this place I wouldn’t have put this here, or that there, etc.” And it’s also something that people can immediately associate themselves with. If I tell you that this game enables you to design theme parks, then you immediately know what I’m talking about.
It was indeed a brilliant stroke, one with natural appeal well beyond the typical gamer demographic who enjoyed the likes of Syndicate. Visually at least, Theme Park would be the polar opposite of that game, cheerful and bright where it had been gritty and dark.
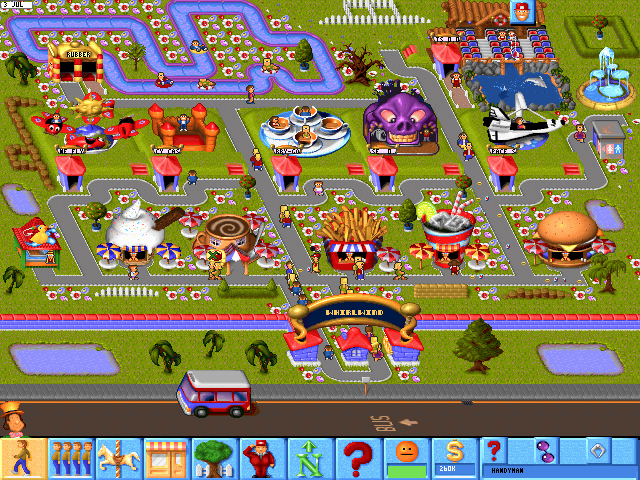
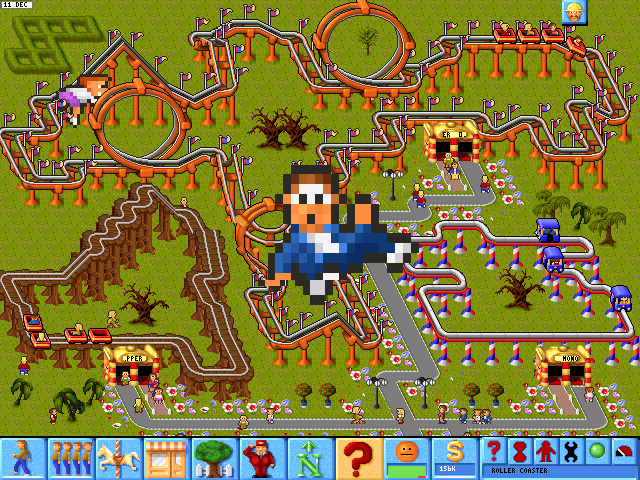
Released in mid-1994, Theme Park became a monster hit — bigger than Syndicate, even bigger than Populous after it was ported to every viable or semi-viable game-playing gadget in the world. Its bright and bouncy visual aesthetic presaged the Casual Revolution in games that was still some years away, while its impact on the themes and mechanics of games to come would prove even more pronounced. In particular, Rollercoaster Tycoon, a direct heir to Theme Park which was released by MicroProse in 1999, sold even better than Bullfrog’s take on the concept — in fact, became one of the best-selling computer games in history. Today amusement parks and roller coasters remain a staple of gaming, from the more elaborate examples of the breed available at online stores like Steam to more easygoing affairs that you can play right in your browser. Almost all of them owe not just a thematic (hah!) debt to Theme Park but a direct mechanical and visual one as well, from the thought bubbles that appear over the heads of the guests wandering through the park to their whimsically cartoony graphical style.
It thus pains even more than usual to note how horribly Theme Park itself has aged, even in comparison to most of the other early Bullfrog games. Few games evidence as profound a mismatch between their surface aesthetics and their underlying gameplay as this one does. The cutesy nature of the former can confuse you for a long time, disguising the fact that the latter really doesn’t represent as great a departure from the worldview of Syndicate as it seems to let on. At bottom, Theme Park is a nasty, cynical little game, amoral if not actively immoral — a game where your concern isn’t with the happiness of your guests at all, but strictly with the amount of money you can extract from them; a profitable theme park with miserable patrons is not only possible but the only practical road to success. This is the kind of game where you over-salt the patrons’ fries to get them to buy more soda, which cups you stuff to the brim with ice to… well, you get the picture. If you come to this game wanting to build a beautiful amusement park and show everybody who visits it a great time, as the Molyneux quote above would imply you can, you’ll wind up bankrupt and disillusioned in extremely short order.
Even if you’re willing to play the game on its own cynical terms, it has all sorts of other problems. There’s a paucity of useful feedback on both a global and granular level, which often puts you in the supremely frustrating position of failing for reasons you can’t determine. The interface in general is inscrutable in too many places, the level of micromanagement required is exhausting, and, because this is a Peter Molyneux game, winning is a task so herculean that virtually no one has ever done so: after building your first successful park in Britain, you’re expected to choose another location elsewhere in the world and do so again, ad nauseum. None of these later parks are different in any fundamental way from the first — you have the exact same rides and shops and food stands at your disposal throughout — and so the whole exercise becomes absurdly repetitive.
Theme Park was a hugely innovative and massively influential game, but it just wasn’t a very good one, even in its heyday. Its appeal was always rooted more in what it purported to be than what it actually managed to be. Because everybody loves a theme park, right?
Bullfrog’s second game of 1994 — also the last one which we’ll be visiting as part of this little survey today — might have appeared at the time to be an attempt to jump onto the 3D-action bandwagon unleashed by Wolfenstein 3D and DOOM. In reality, though, Bullfrog had been experimenting with first-person 3D in-house for years. Those experiments finally led, after many detours and false starts, to Magic Carpet, whose namesake you got to fly — because, as Molyneux wryly put it, every other possible form of flight had already been exhaustively simulated by that point. As one of several wizards, your goal was to build up your arsenal of spells and mana in order to conquer all of the opposing wizards and take over the world. And then — remember, this was a Bullfrog game — you were expected to do the same thing in fifty or so more worlds.
The first Bullfrog game not to be ported at all to lower-powered platforms like the Amiga, Magic Carpet was a stunning technical achievement in its time. While other 3D action games segmented themselves into discrete levels made up of interior spaces only, it gave you a complete open-ended world to explore. It was a forthrightly artsy game, something DOOM and the rash of similar games which followed it certainly never aspired to be. In that spirit, it contained no words during actual gameplay, nothing to distract from the evocative wonder of its world. Bullfrog’s staffers talked in interviews about the joy they got just from drifting around above its landscapes before they’d put any enemies in — playing as they did so, they said only half facetiously, their Enya albums. Magic Carpet even had a special stereoscopic 3D mode, for those able to buy or make 3D glasses to suit.
By the time you got four or five levels into it, however, it revealed itself to suffer from the standard set of Bullfrog problems. Each of its worlds was superficially different from the one before, but not in a way that really challenged you or introduced a sense of progression beyond the increasing level number on your status screen. The game shot its bolt at the beginning, then just kept giving you more of the same. Peter Molyneux spoke often in interviews about his desire to give gamers lots of value for their money by making big games. Yet, like songwriters with a knack for melody who have no clue how to take it to the bridge, he and his mates consistently struggled to find ways of varying their formulas so that their games weren’t just more of the same for hours on end. As it was, what you saw in the first hour of a Bullfrog game was what you would continue to see for the next hundred hours.
And for once, this Bullfrog game’s presentation and theme alone weren’t enough to save it on store shelves. Its abstracted and almost aggressively artsy personality combined with its high production costs and high system requirements to make it Bullfrog’s first outright money loser since Flood.
How, then, should we sum up these five busy years in the life of Peter Molyneux and his first company? We can feel certain that anything we do say must apply almost equally to his career since 1994; whether you love or hate his work, its strengths and weaknesses haven’t changed very much over the decades. An unkind assessment — of which there have been many in the last ten years in particular, as Molyneux’s real or perceived penchant for over-hyping and under-delivering has come home to roost — might peg him as a bit of a dilettante, an ideas man unwilling to do the hard work to turn his ideas into balanced games that remain playable and interesting over the long term. But the reality is, as usual, more complex than any single pejorative — or compliment, for that matter — can encompass.
Some keys to the puzzle of Peter Molyneux can undoubtedly be found in the scene from which he sprang. His design aesthetic, like that of so many British game developers, was to a large extent forged by the limited resources — in terms of both target hardware and finances — which they had at their disposal. Bullfrog’s stubborn reliance on procedurally-generated rather than handcrafted levels, often to their games’ detriment, can be traced back at least to Ian Bell and David Braben’s Elite and the vast eight-galaxy universe it packed into a 32 K BBC Micro via the magic of the Fibonacci sequence. When one didn’t have much space to store handcrafted levels and didn’t have many people to hand to make them, procedural generation seemed the only practical way forward. But Bullfrog stuck with it to the exclusion of other approaches for too long — long after other approaches became viable.
Other pieces of the puzzle are more idiosyncratic to Molyneux himself, a fellow whose own personality was always all but inseparable from that of his company. Already by the mid-1990s, his tendency to stretch himself in too many directions at once was starting to become an issue. During the period of Theme Park and Magic Carpet, Bullfrog also worked on something called Creation, where you would breed predatory fish in an underwater base to attack your rivals on the ocean floor. Molyneux even mooted linking Creation with Magic Carpet: “If you’re playing Magic Carpet, you will be able to jump off the carpet and into the ocean. The computer will then sense whether you have Creation on your hard disk and plunge you straight into that, based totally on the world you were just flying around [in].” Another work in progress, with the highly inadvisable title of MIST (My Incredible Superhero Team), would let you build and control your own superhero: “If you want to make him strong and give him rubber wings and death vision, then you can do that. But of course, they’ve all got their Achilles heel.” And then there was Biosphere, featuring a more elaborate, planet-wide take on genetic engineering along with a fictional context shamelessly ripped off from Douglas Adams, where you would “run a team of genetic and planet engineers who modify planets for shiploads of colonists. Unfortunately for you, the colonists are generally hairdressers and telephone engineers, so when they get there they’re pretty useless — and they’ll probably be eaten by dinosaurs. So you have to protect them.” None of these games were ever completed, despite a substantial amount of time and resources being devoted to each of them. Indeed, as the resources available to him increased, Molyneux’s proclivity for rushing enthusiastically down such blind alleys increased in equal measure.
Molyneux’s passionate prioritization of experimentation over the nuts and bolts of game design made him a less complete designer than, say, a Sid Meier. And yet he, along with other designers of a similar bent, have been scarcely less necessary for the evolution of their medium. Few if any designers have dared to put more new stuff out there than Molyneux, even if often in imperfect form. Such experiments can become the building blocks for more grounded designers to build upon, as the example of the badly flawed Theme Park begetting the absolutely brilliant Rollercoaster Tycoon proves in spades.
Another component of Molyneux’s claim to the status of gaming visionary is more generalized: his complete conviction during the early 1990s that, as he put it, “multiplayer games are the future of gaming.” With the exception only of Theme Park, every Molyneux game from Populous on not only supported multiplayer sessions between players on separate computers[1]Multiplayer Syndicate was made available to the public only in the expansion pack. but was literally designed for it first and foremost. That is to say that a serial or network link-up went into Populous, Powermonger, Populous II, Syndicate, and Magic Carpet long before anyone even began to think about adding a computer opponent. One might even call this fact the perfect riposte to all of my complaints about these Bullfrog games. If you played them alone, you were, in Molyneux’s mind anyway, playing them wrong in some fundamental sense. Complaints about the sameness of a game from level to level no longer carry much weight when you’re playing against that ultimate agent of unpredictability, a fellow human. While the nature of the times dictated that most people played them solo, there are nevertheless all sorts of anecdotes about the sharing of those early Bullfrog games among friends; my favorite might be the teenage next-door neighbors who made a 25-meter cable to run between their bedroom windows so that they could play Populous together every night to their hearts’ content. Stories like these, soon to be joined by tales of multiplayer DOOM, were clear signposts in their day to where much of gaming was heading, just as soon as the world’s telecommunications infrastructure caught up to the designers’ vision.
Bullfrog and Peter Molyneux have ironically suffered the opposite fate from that of the standard clichés about pioneers. Greatly appreciated in their own time for all of the bold new things they attempted to do and be, their games’ practical deficiencies seem all too obvious to our more jaded eyes of today. But, even if we can’t quite praise any one of them as a standalone masterpiece, we can recognize the purpose they served in opening up so much virgin territory for exploration by later, often better games. And if Molyneux himself has sinned by promising too much too often, it should be recognized as well that his transgressions have never had their roots in greed or guile. He just wants to make really, really amazing games — wants to make lots of them, thereby to make lots and lots of people happy. There are worse character flaws to have.
(Sources: Retro Gamer 39, 40, 43, 69, and 71; New Computer Express of January 20 1990, October 27 1990, and May 11 1991; CU Amiga of October 1990, February 1991, December 1991, December 1992, November 1993, January 1994, and February 1994; Computer Gaming World of January 1991, April 1991, and December 1994; The One of April 1990, July 1990, December 1990, May 1991, July 1991, December 1991, May 1992, May 1993, June 1993, December 1993, October 1994, and March 1995; Amiga Format of February 1992, October 1992, 1992 annual, June 1994, and May 1995; Zero of December 1991; Edge of January 1994, June 1994, November 1994, March 1995, May 1995, July 1995, and November 1995; PC Zone of June 1993 and November 1994; PC Review of July 1992; Next Generation premier issue. Video sources include the documentary From Bedrooms to Billions and series 3 episode 3 of Bad Influence.
Populous II, Syndicate, Theme Park, and Magic Carpet are all available as digital purchases from GOG.com.)
Footnotes
| ↑1 | Multiplayer Syndicate was made available to the public only in the expansion pack. |
|---|