As you would imagine, a lot of the things you can do in a comedy game just don’t work when trying to remain serious. You can’t cover up a bad puzzle with a funny line of self-referential dialog. Er, not that I ever did that. But anyway, it was also a challenge to maintain the tone and some semblance of a dramatic arc. Another challenge was cultural — we were trying to build this game in an environment where everyone else was building funny games, telling jokes, and being pretty outlandish. It was like trying to cram for a physics final during a dorm party. It would have been a lot easier to join the party.
— Sean Clark, fifth (and last) project lead on The Dig
On October 17, 1989, the senior staff of LucasArts[1]LucasArts was known as Lucasfilm Games until the summer of 1992. To avoid confusion, I use the name “LucasArts” throughout this article. assembled in the Main House of Skywalker Ranch for one of their regular planning meetings. In the course of proceedings, Noah Falstein, a designer and programmer who had been with the studio almost from the beginning, learned that he was to be given stewardship of an exciting new project called The Dig, born from an idea for an adventure game that had been presented to LucasArts by none other than Steven Spielberg. Soon after that bit of business was taken care of, remembers Falstein, “we felt the room start to shake — not too unusual, we’d been through many earthquakes in California — but then suddenly it got much stronger, and we started to hear someone scream, and some glass crash to the floor somewhere, and most of us dived under the mahogany conference table to ride it out.” It was the Loma Prieta Earthquake, which would kill 63 people, seriously injure another 400, and do untold amounts of property damage all around Northern California.
Perhaps Falstein and his colleagues should have taken it as an omen. The Dig would turn into a slow-motion fiasco that crushed experienced game developers under its weight with the same assiduity with which the earthquake collapsed Oakland’s Nimitz Freeway. When a finished version of the game finally appeared on store shelves in late 1995, one rather ungenerous question would be hard to avoid asking: it took you six years to make this?
In order to tell the full story of The Dig, the most famously troubled project in the history of LucasArts, we have to wind the clock back yet further: all the way back to the mid-1980s, when Steven Spielberg was flying high on the strength of blockbusters like Raiders of the Lost Ark and E.T.: The Extra-Terrestrial. During this period, many years before the advent of Prestige TV, Spielberg approached NBC with a proposal for a new anthology series named Amazing Stories, after the pulp magazine that had been such an incubator of printed science fiction in the 1930s and 1940s. He would direct the occasional episode himself, he promised, but would mostly just throw out outlines which could be turned into reality by other screenwriters and directors. Among those willing to direct episodes were some of the most respected filmmakers in Hollywood: people like Martin Scorsese, Irvin Kershner, Robert Zemeckis, and Clint Eastwood. Naturally, NBC was all over it; nowhere else on the television of the 1980s could you hope to see a roster of big-screen talent anything like that. The new series debuted with much hype on September 29, 1985.
But somehow it just never came together for Amazing Stories; right from the first episodes, the dominant reaction from both critics and the public was one of vague disappointment. Part of the problem was each episode’s running time of just half an hour, or 22 minutes once commercials and credits were factored in; there wasn’t much scope for story or character development in that paltry span of time. But another, even bigger problem was that what story and characters were there weren’t often all that interesting or original. Spielberg kept his promise to serve as the show’s idea man, personally providing the genesis of some 80 percent of the 45 episodes that were completed, but the outlines he tossed off were too often retreads of things that others had already done better. When he had an idea he really liked — such as the one about a group of miniature aliens who help the residents of an earthbound apartment block with their very earthbound problems — he tended to shop it elsewhere. The aforementioned idea, for example, led to the film Batteries Not Included.
The episode idea that would become the computer game The Dig after many torturous twists and turns was less original than that one. It involved a team of futuristic archaeologists digging in the ruins of what the audience would be led to assume was a lost alien civilization. Until, that is, the final shot set up the big reveal: the strange statue the archaeologists had been uncovering would be shown to be Mickey Mouse, while the enormous building behind it was the Sleeping Beauty Castle. They were digging at Disneyland, right here on Planet Earth!
The problem here was that we had seen all of this before, most notably at the end of Planet of the Apes, whose own climax had come when its own trio of astronauts stranded on its own apparently alien world had discovered the Statue of Liberty half-buried in the sand. Thus it was no great loss to posterity when this particular idea was judged too expensive for Amazing Stories to produce. But the core concept of archaeology in the future got stuck in Spielberg’s craw, to be trotted out again later in a very different context.
In the meantime, the show’s ratings were falling off quickly. As soon as the initial contract for two seasons had been fulfilled, Amazing Stories quietly disappeared from the airwaves. It became an object lesson that nothing is guaranteed in commercial media, not even Steven Spielberg’s Midas touch.
Fast-forward a couple of years, to when Spielberg was in the post-production phase of his latest cinematic blockbuster, Indiana Jones and the Last Crusade, which he was making in partnership with his good friend George Lucas. Noah Falstein of the latter’s very own games studio had been drafted to design an adventure game of the movie. Despite his lack of a games studio of his own, Spielberg was ironically far more personally interested in computer games than Lucas; he followed Falstein’s project quite closely, to the point of serving as a sort of unofficial beta tester. Even after the movie and game were released, Spielberg would ring up LucasArts from time to time to beg for hints for their other adventures, or sometimes just to shoot the breeze; he was clearly intrigued by the rapidly evolving world of interactive media. During one of these conversations, he said he had a concept whose origins dated back to Amazing Stories, one which he believed might work well as a game. And then he asked if he could bring it over to Skywalker Ranch. He didn’t have to ask twice.
The story that Spielberg outlined retained futuristic archaeology as its core motif, but wisely abandoned the clichéd reveal of Mickey Mouse. Instead the archaeologists would be on an actual alien planet, discovering impossibly advanced technology in what Spielberg conceived as an homage to the 1950s science-fiction classic Forbidden Planet. Over time, the individual archaeologists would come to distrust and eventually go to war with one another; this part of the plot hearkened back to another film that Spielberg loved, the classic Western The Treasure of the Sierra Madre. Over to you, Noah Falstein — after the unpleasant business of the earthquake was behind everybody, that is.
The offices of LucasArts were filled with young men who had grown up worshiping at the shrines of Star Wars and Indiana Jones, and who now found themselves in the completely unexpected position of going to work every day at Skywalker Ranch, surrounded by the memorabilia of their gods and sometimes by the deities themselves. Their stories of divine contact are always entertaining, not least for the way that they tend to sound more like a plot from one of Spielberg’s films than any plausible reality; surely ordinary middle-class kids in the real world don’t just stumble into a job working for the mastermind of Star Wars, do they? Well, it turns out that in some cases they do. Dave Grossman, an aspiring LucasArts game designer at the time, was present at a follow-up meeting with Spielberg that also included Lucas, Falstein, and game designer Ron Gilbert of Maniac Mansion and Monkey Island fame. His account so magnificently captures what it was like to be a starstruck youngster in those circumstances that I want to quote it in full here.
The Main House at Skywalker is a pretty swanky place, and the meeting is in a boardroom with a table the size of a railroad car, made of oak or mahogany or some other sort of expensive wood. I’m a fidgety young kid with clothes that come pre-wrinkled, and this room makes me feel about as out of place as a cigarette butt in a soufflé. I’m a little on edge just being in here.
Then George and Steven show up and we all say hello. Now, I’ve been playing it cool like it’s no big deal, and I know they’re just people who sneeze and drop forks like everybody else, but… it’s Lucas and Spielberg! These guys are famous and powerful and rich and, although they don’t act like any of those things, I’m totally intimidated. (I should mention that although I’ve been working for George for a year or so at this point, this is only the second time I’ve met him.) I realize I’m really fairly nervous now.
George and Steven chit-chat with each other for a little bit. They’ve been friends a long time and it shows. George seems particularly excited to tell Steven about his new car, an Acura I think – they’re not even available to the public yet, but he’s managed to get the first one off the boat, and it’s parked conspicuously right in front of the building.
Pretty soon they start talking about ideas for The Dig, and they are Rapid-Fire Machine Guns of Creativity. Clearly they do this a lot. It’s all very high-concept and all over the map, and I have no idea how we’re going to make any of it into a game, but that’s kind of what brainstorming sessions are all about. Ron and Noah offer up a few thoughts. I have a few myself, but somehow I don’t feel worthy enough to break in with them. So I sit and listen, and gradually my nervousness is joined by embarrassment that I’m not saying anything.
A snack has been provided for the gathering, some sort of crumbly carbohydrate item, corn bread, if I remember correctly. So I take a piece – I’m kind of hungry, and it gives me something to do with my hands. I take a bite. Normally, the food at Skywalker Ranch is absolutely amazing, but this particular corn bread has been made extra dry. Chalk dry. My mouth is already parched from being nervous, so it takes me a while before I’m able to swallow the bite, and as I chomp and smack at it I’m sure I’m making more noise than a dozen weasels in a paper bag, even though everyone pretends not to notice. There are drinks in the room, but they have been placed out of the way, approximately a quarter-mile from where we’re sitting, and I can’t get up to get one without disrupting everything, and I’m sure by now George and Steven are wondering why I’m in the meeting in the first place.
I want to abandon the corn bread, but it’s begun falling apart, and I can’t put it down on my tiny napkin without making a huge mess. So I eat the whole piece. It takes about twenty minutes. I myself am covered with tiny crumbs, but at least there aren’t any on the gorgeous table.
By now the stakes are quite high. Because I’ve been quiet so long, the mere fact of my speaking up will be a noteworthy event, and anything I say has to measure up to that noteworthiness. You can’t break a long silence with a throwaway comment, it has to be a weighty, breathtaking observation that causes each person in the room to re-examine himself in its light. While I’m waiting for a thought that good, more time goes by and raises the bar even higher. I spend the rest of the meeting in a state of near-total paralysis, trying to figure out how I can get out of the room without anyone noticing, or, better yet, how I can go back in time and arrange not to be there in the first place.
So, yes, I did technically get to meet Steven Spielberg face-to-face once while we were working on The Dig. I actually talked to him later on, when he called to get hints on one of our other games (I think it was Day of the Tentacle), which he was playing with his son. (One of the lesser-known perks of being a famous filmmaker is that you can talk directly to the game designers for hints instead of calling the hint line.) Nice guy.
The broader world of computer gaming’s reaction to Spielberg’s involvement in The Dig would parallel the behavior of Dave Grossman at this meeting. At the same time that some bold industry scribes were beginning to call games a more exciting medium than cinema, destined for even more popularity thanks to the special sauce of interactivity, the press that surrounded The Dig would point out with merciless clarity just how shallow their bravado was, how deep gaming’s inferiority complex really ran: Spielberg’s name was guaranteed to show up in the first paragraph of every advertisement, preview, or, eventually, review. “Steven Spielberg is deigning to show an interest in little old us!” ran the implicit message.
It must be said that the hype was somewhat out of proportion to his actual contribution. After providing the initial idea for the game — an idea that would be transformed beyond all recognition by the time the game was released — Spielberg continued to make himself available for occasional consultations; he met with Falstein and his colleagues for four brainstorming sessions, two of which also included his buddy George Lucas, over the course of about eighteen months. (Thanks no doubt to the prompting of his friend, Lucas’s own involvement with The Dig was as hands-on as he ever got with one of his games studio’s creations.) Yet it’s rather less clear whether these conversations were of much real, practical use to the developers down in the trenches. Neither Spielberg nor Lucas was, to state the obvious, a game designer, and thus they tended to focus on things that might yield watchable movies but were less helpful for making a playable game. Noah Falstein soon discovered that heading a project which involved two such high-profile figures was a less enviable role than he had envisioned it to be; he has since circumspectly described a project where “everyone wanted to put their two cents in, and that can be extremely hard to manage.”
In his quest for a game that could be implemented within the strictures of SCUMM, LucasArts’s in-house point-and-click adventure engine, Falstein whittled away at Spielberg’s idea of two teams of archaeologists who enter into open war with one another. His final design document, last updated on January 30, 1991, takes place in “the future, nearly 80 years since the McKillip Drive made faster-than-light travel a possibility, and only 50 years since the first star colonies were founded.” In another nod back to Spielberg’s old Amazing Stories outline that got the ball rolling, an unmanned probe has recently discovered an immense statue towering amidst other alien ruins on the surface of a heretofore unexplored planet; in a nod to the most famous poem by Percy Shelley, the planet has been named Ozymandias. Three humans have now come to Ozymandias to investigate the probe’s findings — but they’re no longer proper archaeologists, only opportunistic treasure hunters, led by a sketchy character named Major Tom (presumably a nod to David Bowie). The player can choose either of Major Tom’s two subordinates as her avatar.
A series of unfortunate events ensues shortly after the humans make their landing, over the course of which Major Tom is killed and their spaceship damaged beyond any obvious possibility of repair. The two survivors have an argument and go their separate ways, but in this version of the script theirs is a cold rather than a hot war. As the game goes on, the player discovers that a primitive race of aliens living amidst the ruins are in fact the descendants of far more advanced ancestors, who long ago destroyed their civilization and almost wiped out their entire species with internecine germ warfare. But, the player goes on to learn, there are survivors of both factions who fought the apocalyptic final war suspended in cryogenic sleep beneath the surface of the planet. Her ultimate goal becomes to awaken these survivors and negotiate a peace between them, both because it’s simply the right thing to do and because these aliens should have the knowledge and tools she needs to repair her damaged spaceship.

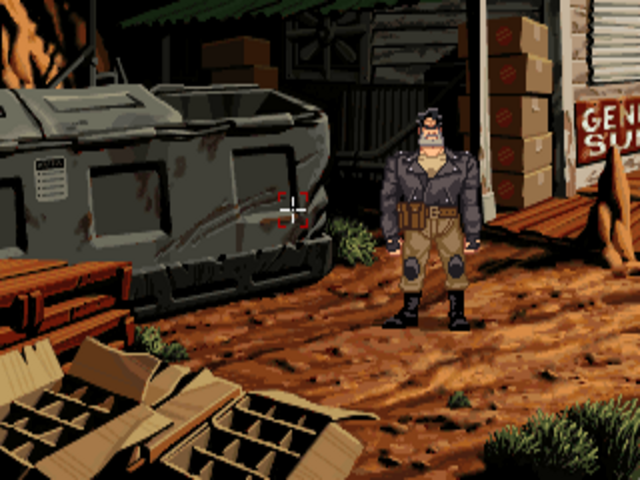
This image by Ken Macklin is one of the few pieces of concept art to have survived from Noah Falstein’s version of The Dig.
For better or for worse, this pared-down but still ambitious vision for The Dig never developed much beyond that final design document and a considerable amount of accompanying concept art. “There was a little bit of SCUMM programming done on one of the more interesting puzzles, but not much [more],” says Falstein. He was pulled off the project very early in 1991, assigned instead to help Hal Barwood with Indiana Jones and the Fate of Atlantis. And when this, his second Indiana Jones game, was finished, he was laid off despite a long and largely exemplary track record.
Meanwhile The Dig spent a year or more in limbo, until it was passed to Brian Moriarty, the writer and designer of three games for the 1980s text-adventure giant Infocom and of LucasArts’s own lovely, lyrical Loom. Of late, he’d been drafting a plan for a game based on The Young Indiana Jones Chronicles, the franchise’s slightly disappointing foray into television, but a lack of personal enthusiasm for the project had led to a frustrating lack of progress. Moriarty was known as one of the most “literary” of game designers by temperament; his old colleagues at Infocom had called him “Professor Moriarty,” more as a nod to his general disposition than to the milieu of Sherlock Holmes. And indeed, his Trinity is as close as Infocom ever got to publishing a work of high literature, while his Loom possesses almost an equally haunting beauty. Seeing himself with some justification as a genuine interactive auteur, he demanded total control of every aspect of The Dig as a condition of taking it on. Bowing to his stellar reputation, LucasArts’s management agreed.
Much of what went on during the eighteen months that Moriarty spent working on The Dig remains obscure, but it plainly turned into a very troubled, acrimonious project. He got off on the wrong foot with many on his team by summarily binning Falstein’s vision — a vision which they had liked or even in some cases actively contributed to. Instead he devised an entirely new framing plot.
Rather than the far future, The Dig would now take place in 1998; in fact, its beginning would prominently feature the Atlantis, a Space Shuttle that was currently being flown by NASA. A massive asteroid is on a collision course with Earth. Humanity’s only hope is to meet it in space and plant a set of nuclear bombs on its surface. Once exploded, they will hopefully deflect the asteroid just enough to avoid the Earth. (The similarity with not one but two terrible 1998 movies is presumably coincidental.) You play Boston Low, the commander of the mission.
But carrying the mission out successfully and saving the Earth is only a prelude to the real plot. Once you have the leisure to explore the asteroid, you and your crew begin to discover a number of oddities about it, evidence that another form of intelligent being has been here before you. In the midst of your investigations, you set off a booby trap which whisks you and three other crew members light years away to a mysterious world littered with remnants of alien technology but bereft of any living specimens. Yet it’s certainly not bereft of danger: one crew member gets killed in gruesome fashion almost immediately when he bumbles into a rain of acid. Having thus established its bona fides as a serious story, a million light years away from the typical LucasArts cartoon comedy, the game now begins to show a closer resemblance to Falstein’s concept. You must explore this alien world, solve its puzzles, and ferret out the secrets of the civilization that once existed here if you ever hope to see Earth again. In doing so, you’re challenged not only by the environment itself but by bickering dissension in your own ranks.
This last element of the plot corresponded uncomfortably with the mood inside the project. LucasArts had now moved out of the idyllic environs of Skywalker Ranch and into a sprawling, anonymous office complex, where the designers and programmers working on The Dig found themselves in a completely separate building from the artists and administrators. Reading just slightly between the lines here, the root of the project’s troubles seems to have been a marked disconnect between the two buildings. Moriarty, who felt compelled to create meaningful, thematically ambitious games, became every accountant and project planner’s nightmare, piling on element after element, flying without a net (or a definitive design document). He imagined an interface where you would be able to carry ideas around with you like physical inventory items, a maze that would reconfigure itself every time you entered it, a Klein bottle your characters would pass through with strange metaphysical and audiovisual effects. To make all this happen, his programmers would need to create a whole new game engine of their own rather than relying on SCUMM. They named it StoryDroid.

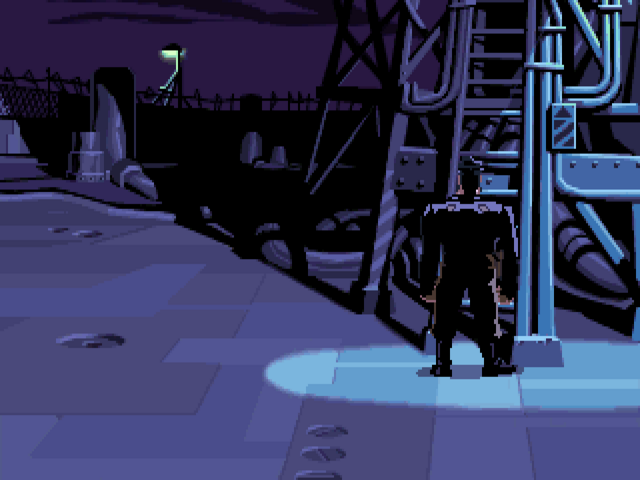
A screenshot from Moriarty’s version of The Dig. Note the menu of verb icons at the bottom of the screen. These would disappear from later versions in favor of the more streamlined style of interface which LucasArts had begun to employ with Sam and Max Hit the Road.
There were some good days on Moriarty’s Dig, especially early on. Bill Tiller, an artist on the project, recalls their one in-person meeting with Steven Spielberg, in his office just behind the Universal Studios Theme Park. Moriarty brought a demo of the work-in-progress, along with a “portable” computer the size of a suitcase to run it. And he also brought a special treat for Spielberg, who continued to genuinely enjoy games in all the ways George Lucas didn’t. Tiller:
Brian brought an expansion disk for one of the aerial battle games Larry Holland was making. Spielberg was a big computer-game geek! He was waiting for this upgrade/mission expansion thing. He called his assistant in and just mentioned what it was. She immediately knew what he meant and said she’d send it home and tell someone to have it installed and running for him when he arrived. I decided at that moment I would have an assistant like that someday.
Anyway, when we were through we told him we had a few hours to kill and wondered what rides we should get on back at the theme park. He said the E.T. ride, since he helped design it. It was brand new at the time. His people said that he was really crazy about it and wanted to show it off to everyone. One of his assistants took us there on a back-lot golf cart. We didn’t have to get another taxi. We didn’t even have to stand in line! They took us straight to the ride and cut us in the line in front of everyone, like real V.I.P.s. Everyone had to stand back and watch, probably trying to figure out who we were. All I remember is Brian with the stupid giant suitcase going through the ride.
But the best part of the whole thing for me was [Spielberg’s] enthusiasm. He really likes games. This wasn’t work to him to have to hear us go on about The Dig.
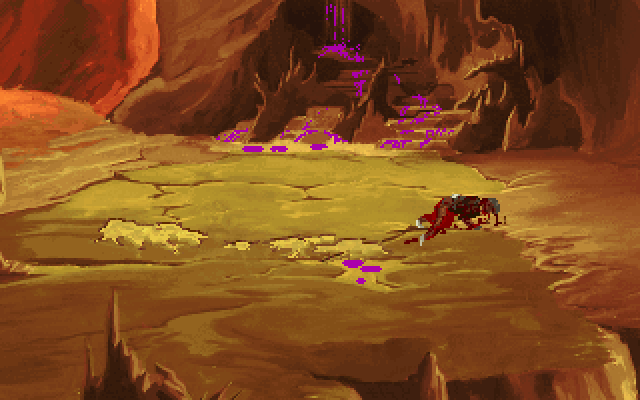

Brian Moriarty’s version of The Dig was more violent than later versions, a quality which Steven Spielberg reportedly encouraged. Here an astronaut meets a gruesome end after being exposed to an alien acid rain.
But the bonhomie of the Universal Studios visit faded as the months wore on. Moriarty’s highfalutin aspirations began to strike others on the team — especially the artists who were trying to realize his ever-expanding vision — as prima-donna-ish; at the end of the day, after all, it was just a computer game they were making. “I used to tell Brian, when he got all excited about what people would think of our creation, that in ten years no one will even remember The Dig,” recalls Bill Eaken, the first head artist to work under him. He believes that Moriarty may even have imagined Spielberg giving him a screenwriting or directing job if The Dig sufficiently impressed him. Eaken:
I liked Brian. Brian is a smart and creative guy. I still have good memories of sitting in his office and just brainstorming. The sky was the limit. That’s how it should be. Those were good times. But I think as time went on he had stars in his eyes. I think he wanted to show Spielberg what he could do and it became too much pressure on him. After a while he just seemed to bog down under the pressure. When all the politics and Hollywood drama started to impede us, when it wasn’t even a Hollywood gig, I [got] temperamental.
The programming was a complete disaster. I had been working for several years at LucasArts at that time and had a very good feel for the programming. I taught programming in college, and though I wasn’t a programmer on any games, I understood programming enough to know something was amiss on The Dig. I went to one of my friends at the company who was a great programmer and told him my concerns. He went and tried to chat with the programmers about this or that to get a look at their code, but whenever he walked into the room they would shut off their monitors, things like that. What he could see confirmed my worries: the code was way too long, and mostly not working.
The project was “completely out of control and management wouldn’t listen to me about it,” Eaken claims today. So, he quit LucasArts, whereupon his role fell to his erstwhile second-in-command, the aforementioned Bill Tiller. The latter says that he “liked and disliked” Moriarty.
Brian was fun to talk with and was very energetic and was full of good ideas, but he and I started to rub each other the wrong way due to our disagreement over how the art should be done. I wanted the art organized in a tight budget and have it all planned out, just like in a typical animation production, and so did my boss, who mandated I push for an organized art schedule. Brian bristled at being restricted with his creativity. He felt that the creative process was hindered by art schedules and strict budgets. And he was right. But the days of just two or three people making a game were over, and the days of large productions and big budgets were dawning, and I feel Brian had a hard time adjusting to this new age.
Games were going through a transition at that time, from games done by a few programmers with little art, to becoming full-blown animated productions where the artists outnumber the programmers four to one. Add to the mix the enormous pressure of what a Spielberg/Lucas project should be like [and] internal jealousy about the hype, and you have a recipe for disaster.
He wanted to do as much of the game by himself as possible so that it was truly his vision, but I think he felt overwhelmed by the vastness of the game, which required so much graphics programming and asset creation. He was used to low-res graphics and a small intimate team of maybe four people or less. Then there is the pressure of doing the first Spielberg/Lucas game. I mean, come on! That is a tough, tough position for one guy to be in.
One of LucasArt’s longstanding traditions was the “pizza orgy,” in which everyone was invited to drop whatever they were doing, come to the main conference room, eat some pizza, and play a game that had reached a significant milestone in its development. The first Dig pizza orgy, which took place in the fall of 1993, was accompanied by an unusual amount of drama. As folks shuffled in to play the game for the very first time, they were told that Moriarty had quit that very morning.
We’re unlikely ever to know exactly what was going through Moriarty’s head at this juncture; he’s an intensely private individual, as it is of course his right to be, and is not at all given to baring his soul in public. What does seem clear, however, is that The Dig drained from him some fragile reservoir of heedless self-belief which every creative person needs in order to keep creating. Although he’s remained active in the games industry in various roles, those have tended to be managerial rather than creative; Brian Moriarty, one of the best pure writers ever to explore the potential of interactive narratives, never seriously attempted to write another one of them after The Dig. In an interview he did in 2006 for Jason Scott’s film Get Lamp, he mused vaguely during a pensive interlude that “I’m always looking for another Infocom. But sometimes I think we won’t give ourselves permission.” (Who precisely is the “we” here?) This statement may, I would suggest, reveal more than Moriarty intended, about more of his career than just his time at Infocom.
At any rate, Moriarty left LucasArts with one very unwieldy, confused, overambitious project to try to sort out. It struck someone there as wise to give The Dig to Hal Barwood, a former filmmaker himself who had been friends with Steven Spielberg for two decades. But Barwood proved less than enthusiastic about it — which was not terribly surprising in light of how badly The Dig had already derailed the careers of two of LucasArts’s other designers. Following one fluffy interview where he dutifully played up the involvement of Spielberg for all it was worth — “We’re doing our best to capture the essence of the experience he wants to create” — he finagled a way off the project.
At this point, the hot potato was passed to Dave Grossman, who had, as noted above, worked for a time with Noah Falstein on its first incarnation. “I was basically a hedge trimmer,” he says. “There was a general feeling, which I shared, that the design needed more work, and I was asked to fix it up while retaining as much as possible of what had been been done so far — starting over yet again would have been prohibitively expensive. So I went in with my editing scissors, snip snip snip, and held a lot of brainstorming meetings with the team to try to iron out the kinks.” But Grossman too found something better to do as quickly as possible, whereupon the game lay neglected for the better part of a year while much of Moriarty’s old team went to work on Tim Schafer’s Full Throttle: “a project that the company loved,” says Bill Tiller, drawing an implicit comparison with this other, unloved one.
In late 1994, The Dig was resurrected for the last time, being passed to Sean Clark, a long-serving LucasArts programmer who had moved up to become the producer and co-designer of Sam and Max Hit the Road, and who now saw becoming the man who finally shepherded this infamously vexed project to completion as a good way to continue his ascent. “My plan when I came in on the final incarnation was to take a game that was in production and finish it,” he says. “I didn’t get a lot of pressure or specific objectives from management. I think they were mainly interested in getting the project done so they could have a product plan that didn’t have The Dig listed on it.” Clark has admitted that, when he realized what a sorry state the game was actually in, he went to his bosses and recommended that they simply cancel it once and for all. “I got a lot of resistance, which surprised me,” he says. “It was hard to resist the potential [of having] a game out there with a name like Spielberg’s on it.” In a way, George Lucas was a bigger problem than Spielberg in this context: no one wanted to go to the boss of bosses at LucasArts and tell him they had just cancelled his close friend’s game.
Sean Clark with a hot slice. Pizza was a way of life at LucasArts, as at most games studios. Asked about the negative aspects of his job, one poor tester said that he was “getting really, really tired of pizza. I just can’t look at pizza anymore.”
So, Clark rolled up his sleeves and got to work instead. His first major decision was to ditch the half-finished StoryDroid engine and move the project back to SCUMM. He stuck to Brian Moriarty’s basic plot and characters, but excised without a trace of hesitation or regret anything that was too difficult to implement in SCUMM or too philosophically esoteric. His goal was not to create Art, not to stretch the boundaries of what adventure games could be, but just to get ‘er done. Bill Tiller and many others from the old team returned to the project with the same frame of reference. By now, LucasArts had moved offices yet again, to a chic new space where the programmers and artists could mingle: “Feedback was quick and all-encompassing,” says Tiller. If there still wasn’t a lot of love for the game in the air, there was at least a measure of esprit de corps. LucasArts even sprang for a couple more (reasonably) big names to add to The Dig‘s star-studded marque, hiring the science-fiction author Orson Scott Card, author of the much-admired Ender’s Game among other novels, to write the dialogue, and Robert Patrick, Arnold Schwarzenegger’s principal antagonist from Terminator 2, to head up the cast of voice actors. Remarkably in light of how long the project had gone on and how far it had strayed from his original vision, Steven Spielberg took several more meetings with the team. “He actually called me at home one evening as he was playing through a release candidate,” says Sean Clark. “He was all excited and having fun, but was frustrated because he had gotten stuck on a puzzle and needed a hint.”
Clark’s practicality and pragmatism won the day where the more rarefied visions of Falstein and Moriarty had failed: The Dig finally shipped just in time for the Christmas of 1995. LucasArts gave it the full-court press in terms of promotion, going so far as to call it their “highest-profile product yet.” They arranged for a licensed strategy guide, a novelization by the king of tie-in novelists Alan Dean Foster, an “audio drama” of his book, and even a CD version of Michael Land’s haunting soundtrack to be available within weeks of the game itself. And of course they hyped the Spielberg connection for all it was worth, despite the fact that the finished game betrayed only the slightest similarity to the proposal he had pitched six years before.

Composer Michael Land plays timpani for The Dig soundtrack. One can make a strong argument that his intensely atmospheric, almost avant-garde score is the best thing about the finished game. Much of it is built from heavily processed, sometimes even backwards-playing samples of Beethoven and Wagner. Sean Clark has described, accurately, how it sounds “strange and yet slightly familiar.”
But the reaction on the street proved somewhat less effusive than LucasArts might have wished. Reviews were surprisingly lukewarm, and gamers were less excited by the involvement of Steven Spielberg than the marketers had so confidently predicted. Bill Tiller feels that the Spielberg connection may have been more of a hindrance than a help in the end: “Spielberg’s name was a tough thing to have attached to this project because people have expectations associated with him. The general public thought this was going to be a live-action [and/or] 3D interactive movie, not an adventure game.” The game wasn’t a commercial disaster, but sold at less than a third the pace of Full Throttle, its immediate predecessor among LucasArts adventures. Within a few months, the marketers had moved on from their “highest-profile product yet” to redouble their focus on the Star Wars games that were accounting for more and more of LucasArts’s profits.
One can certainly chalk up some of the nonplussed reaction to The Dig to its rather comprehensive failure to match the public’s expectations of a LucasArts adventure game. In a catalog that consisted almost exclusively of cartoon comedies, it was a serious, even gloomy game. In a catalog of anarchically social, dialog-driven adventures that were seen by many gamers as the necessary antithesis to the sterile, solitary Myst-style adventure games that were now coming out by the handful, it forced you to spend most of its length all alone, solving mechanical puzzles that struck many as painfully reminiscent of Myst. Additionally, The Dig‘s graphics, although well-composed and well-drawn, reflected the extended saga of its creation; they ran in low-resolution VGA at a time when virtually the whole industry had moved to higher-resolution Super VGA, and they reflected as well the limitations of the paint programs and 3D-rendering software that had been used to create them, in many cases literally years before the game shipped. In the technology-obsessed gaming milieu of the mid-1990s, when flash meant a heck of a lot, such things could be ruinous to a new release’s prospects.
But today, we can presumably look past such concerns to the fundamentals of the game that lives underneath its surface technology. Unfortunately, The Dig proves far from a satisfying experience even on these terms.
An adventure game needs to be, if nothing else, reasonably good company, but The Dig fails this test. In an effort to create “dramatic” characters, it falls into the trap of merely making its leads unlikable. All of them are walking, talking clichés: the unflappable Chuck Yeager-type who’s in charge, the female overachiever with a chip on her shoulder who bickers with his every order, the arrogant German scientist who transforms into the villain of the piece. Orson Scott Card’s dialog is shockingly clunky, full of tired retreads of action-movie one-liners; one would never imagine that it comes from the pen of an award-winning novelist if it didn’t say so in the credits. And, even more unusually for LucasArts, the voice acting is little more inspired. All of which is to say that it comes as something of a relief when everyone else just goes away and leaves Boston Low alone to solve puzzles, although even then you still have to tolerate Robert Patrick’s portrayal of the stoic mission commander; he approaches an unknown alien civilization on the other side of the galaxy with all the enthusiasm of a gourmand with a full belly reading aloud from a McDonald’s menu.
Alas, one soon discovers that the puzzle design isn’t any better than the writing or acting. While the puzzles may have some of the flavor of Myst, they evince none of that game’s rigorous commitment to internal logic and environmental coherence. In contrast to the free exploration offered by Myst, The Dig turns out to be a quite rigidly linear game, with only a single path through its puzzles. Most of these require you just to poke at things rather than to truly enter into the logic of the world, meaning you frequently find yourself “solving” them without knowing how or why.
But this will definitely not happen in at least two grievous cases. At one point, you’re expected to piece together an alien skeleton from stray bones when you have no idea what said alien is even supposed to look like. And another puzzle, involving a cryptic alien control panel, is even more impossible to figure out absent hours of mind-numbing trial and error. “I had no clue that was such a hard puzzle,” says Bill Tiller. “We all thought it was simple. Boy, were we wrong.” And so we learn the ugly truth: despite the six years it spent in development, nobody ever tried to play The Dig cold before it was sent out the door. It was the second LucasArts game in a row of which this was true, indicative of a worrisome decline in quality control from a studio that had made a name for themselves by emphasizing good design.
At the end of The Dig, the resolution of the alien mystery is as banal as it is nonsensical, a 2001: A Space Odyssey with a lobotomy. It most definitely isn’t “an in-depth story in which the exploration of human emotion plays as important a role as the exploration of a game world,” as LucasArts breathlessly promised.
So, The Dig still manages to come across today as simultaneously overstuffed and threadbare. It broaches a lot of Big Ideas (a legacy of Falstein and Moriarty’s expansive visions), but few of them really go anywhere (a legacy of Grossman and Clark’s pragmatic trimming). It winds up just another extended exercise in object manipulation, but it doesn’t do even this particularly well. Although its audiovisuals can create an evocative atmosphere at times, even they come across too often as disjointed, being a hodgepodge of too many different technologies and aesthetics. Long experience has taught many of us to beware of creative expressions of any stripe that take too long to make and pass through too many hands in the process. The Dig only proves this rule: it’s no better than its tortured creation story makes you think it will be. Its neutered final version is put together competently, but not always well, and never with inspiration. And so it winds up being the one thing a game should never be: it’s just kind of… well, boring.
As regular readers of this site are doubtless well aware, I’m a big fan of LucasArts’s earlier adventures of the 1990s. The one complaint I’ve tended to ding them with is a certain failure of ambition — specifically, a failure to leave their designers’ wheelhouse of cartoon comedy. And yet The Dig, LucasArts’s one concerted attempt to break that mold, ironically winds up conveying the opposite message: that sometimes it’s best just to continue to do what you do best. The last of their charmingly pixelated “classic-look” adventure games, The Dig is sadly among the least satisfying of the lot, with a development history far more interesting than either its gameplay or its fiction. A number of people looked at it with stars in their eyes over the six years it remained on LucasArts’s list of ongoing projects, but it proved a stubbornly ill-starred proposition for all of them in the end.
(Sources: the book The Dig: Official Player’s Guide by Jo Ashburn; Computer Gaming World of March 1994, September 1994, September 1995, October 1995, December 1995, and February 1996; Starlog of October 1985; LucasArts’s customer newsletter The Adventurer of Spring 1993, Winter 1994, Summer 1994, Summer 1995, and Winter 1995. Online sources include Noah Falstein’s 2017 interview on Celebrity Interview, Falstein’s presentation on his history with Lucasfilm Games for Øredev 2017, the “secret history” of The Dig at International House of Mojo, the same site’s now-defunct “Dig Museum,” ATMachine’s now-defunct pages on the game, Brian Moriarty’s 2006 interview for Adventure Classic Gaming, and Moriarty’s Loom postmortem at the 2015 Game Developers Conference. Finally, thank you to Jason Scott for sharing his full Get Lamp interview archives with me years ago.
The Dig is available for digital purchase on GOG.com.)
Footnotes
| ↑1 | LucasArts was known as Lucasfilm Games until the summer of 1992. To avoid confusion, I use the name “LucasArts” throughout this article. |
|---|
























