That’s the challenge: giving the public a formula they know and feel comfortable with, but making it different from anything they’ve seen or experienced before.
— Roberta Williams
Although Ken Williams left his office at Sierra On-Line for the last time on November 1, 1997, his wife Roberta Williams stayed on for another year, working on the eighth entry in her iconic King’s Quest series. King’s Quest: Mask of Eternity turned into the most protracted and tortured project of her long career.
Roberta had long since fallen into a pattern of alternating new King’s Quest games with other, original creations. Thus after Phantasmagoria shipped in the summer of 1995, it was time for her to begin to sculpt a King’s Quest VIII. Yet she was unusually slow to get going in earnest this time around; perhaps she was feeling some of the same sense of exhaustion that her husband was struggling with in a very different professional context. She tinkered with ideas for the better part of a year, during which the fateful acquisition of Sierra by CUC came to pass. By the time a team was finally assembled around her to make King’s Quest: Mask of Eternity in mid-1996, Sierra’s day-to-day operations were teetering on the cusp of enormous changes, not the least of which would be Ken Williams’s dramatically circumscribed authority. To further punctuate the sense of a new era in the offing, Mask of Eternity was to be the first King’s Quest game ever not to be made in Oakhurst, California; this one would come out of the new offices in Bellevue, Washington. Most members of the team assigned to it were new as well, with the most prominent exception being producer Mark Seibert, who had filled the same role on the hugely successful King’s Quest VII: The Princeless Bride and Phantasmagoria.
By this point, the lack of any subsequent point-and-click adventure games that had sold in similar numbers to Phantasmagoria, from Sierra or anyone else, was sufficient to raise concerns about the genre’s health in any thoughtful observer of the state of the industry. Roberta Williams apparently was such an observer, for it was she herself who decided to make Mask of Eternity different from all of the King’s Quest games that had come before, in order to better meet the desires of contemporary gamers as she understood them. Using Mark Seibert, who had played a lot more of the recent popular non-adventure games than she had, as something of a spirit guide to the new normal, she conceived a King’s Quest that would run in a real-time 3D engine, combining her usual focus on storytelling and puzzle-solving with some action elements. The broader goal would be to create a dynamic living world full of emergent potential, rather than another collection of set-piece puzzles linked together by semi-interactive conversations and non-interactive cutscenes. “We didn’t want to make it so you go here and solve a puzzle, then go there to solve a puzzle, then go to a puzzle somewhere else,” she told an early journalist on the scene. “What we really wanted to bring was that sense of going on an adventure, of going on a quest. It’s not just a word in the title. We want you to feel like you’re really doing it.”
Taken in the abstract, her understanding of what she needed to do in order to keep King’s Quest relevant wasn’t by any means completely misguided. Yet circumstances almost immediately began to militate against it cohering into a solid, playable game. SCI, the venerable adventure engine that had powered the last four King’s Quest games and Phantasmagoria, along with dozens of other products from Sierra, was totally unsuited for this one. To replace it, the team wound up borrowing a 3D engine that had been developed by Sierra’s subsidiary Dynamix with flight simulators in mind. They never were able to fully wrestle it into a form suitable for this application; the finished game remains a festival of jank, sporting walls that you can literally walk right through if you hit them just right.
Roberta Williams felt her own authority being gradually undermined as the new order at Sierra, now merely one part of the software arm of CUC, became a fact of life. In the past, she had enjoyed privileges that were granted to none of Sierra’s other designers — such were the benefits of sleeping with the boss, as she herself sometimes joked. She had worked from home most days, emailing her design documents to the people entrusted with implementing them and then supervising their labor only loosely from afar. But she now found that her ability to set her own working hours and location and even to make fundamental decisions about her own game was waning in tandem with her husband’s fading star. “Suddenly finding that she was expected to build another bestselling King’s Quest game, but that the developers didn’t really have to do what she said, was something Roberta had never had to face,” writes Ken in his memoir. “There were days when she would come home crying.”
In the last week of 1996, Blizzard Entertainment, that rising star of the CUC software arm, shipped Diablo to instant, smashing success. A decree came down from above to make Mask of Eternity more like Diablo, by adding extensive monster-killing and other CRPG-like elements to the design. Roberta Williams was utterly out of her depth. Increasingly, she felt like a third wheel on her own bicycle. And yet there was no other confident and empowered voice and vision to replace hers, just a babble of opinions — hers among them, of course — trying to arrive at some sort of consensus on every new question that came up. Whatever his other faults as an administrator and organizer, Ken Williams had never allowed this to happen. His rule had always been that there was one lead designer on each project, and that person called the shots. If the lead designer “wanted something done, whether the team agreed or not, it didn’t matter. It’s her game and her career on the line.” Now, though, this philosophy no longer held sway at Sierra, even as there was no coherent alternative one to take its place.
So, the Mask of Eternity team bumbled along with no clear ship date in sight, more a mob of wayward peasants than a well-honed army. In the meantime, there were more big changes at the corporate level: as we learned in the last article, the merger of CUC with HFS was announced in May of 1997. It was to be consummated that December, with the conjoined corporation taking the name of “Cendant,” from the Latin root that has given us the verb “to ascend” in English. The name was chosen by Walter Forbes, reflecting the conceit of a culture-vulture sophisticate in which he so loved to cloak himself. For his part, Henry Silverman of HFS, who was all about facts and figures and bottom lines, thought one name was as good as another, as long as his marketing people told him it would pass muster on Wall Street.
Well before the merger was completed, there were signs that this shotgun marriage of opposites was going to be a more challenging relationship than either had anticipated. Silverman ran a tight, focused ship, while Forbes’s board of directors and senior managers were, as Ken Williams had experienced firsthand, more inclined to discuss their golf handicaps than matters of vital interest to the company. “They were like children playing at business,” says one of Silverman’s top lieutenants of his counterparts from CUC. Growing concerned about the overall competence level and work ethic of Forbes himself, Silverman suggested to him in November of 1997, before the merger was even completed, that it might be best if he, Silverman, stayed on a little longer as CEO instead of turning over that position on January 1, 2000, as stipulated in the merger contract.
This was not music to Forbes’s ears. He had already been complaining for a while about Silverman’s high-handed style — about the way he was treating CUC as if it was being bought rather than being an equal partner in a merger — and he didn’t even deign to reply to this latest proof of his allegations. The relationship between the two executives grew so poisonous that Silverman hired a private detective to investigate rumors of womanizing and sexual harassment on Forbes’s part, hoping to find some leverage to use against him. Much to his disappointment, the detective failed to dig up enough actionable dirt.
Again, it should be remembered that all of this jockeying was taking place before the merger had even come off. Given the warning signs that were blinking red everywhere by November, one does wonder why Henry Silverman went through with the deal. The best answer anyone has come up with is that he was a creature of the stock market right down to his bones, and both companies’ stock prices had been sent soaring by the news of the merger. To call it off now would cause the stock to crater just as quickly.
So, the marriage was consummated on schedule, with Henry Silverman as the first CEO of the new Cendant Corporation. By virtue of his job title, he ought to have had access to every aspect of the former CUC’s operations and finances. Yet he ran into a baffling resistance from Forbes’s middle managers whenever he tried to dig beneath the surface. When he called on Forbes directly to intercede and get him the numbers he wanted, Forbes said blithely that he would prefer to preserve the “financial-reporting autonomy” of his half of the company. Silverman, whose temper could be volcanic, had to expend great effort to keep it under control now. He explained to his new chairman of the board, as clearly and calmly as he could, that that wasn’t how a merger worked. Forbes seemed to accept this. And yet at the end of February, more than two months after the merger had ostensibly been effected, Silverman still had no clear figures on his desk. His accountants were now telling him that, if these didn’t surface soon, they would be unable to make a legally mandated filing with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Silverman would have to be a far less perceptive businessman than he was not to smell a rat of considerable proportions.
On March 6, 1998, he dispatched his chief accounting officer Scott Forbes — no relation to Walter — from Cendant’s new headquarters in Manhattan to CUC’s old ones in Stamford, Connecticut. The accountant’s orders were to get the numbers he needed by any means necessary, even if it required getting Silverman himself to come onto the speakerphone and threaten somebody’s job. He met with E. Kirk Shelton, Walter Forbes’s right-hand man. Caving at last, Shelton sheepishly explained that there was a little problem — only a little one, mind you — with the former CUC’s books. Its actual revenues during its last year had come in about $165 million under the figures it had reported. While Scott Forbes was still shaking his head at this piece of news, wondering if he had heard correctly, Shelton rushed to add that the problem was easily fixable, by reporting equity from the merger as operating revenue. “We want you to help us figure out how to creatively do this,” said Shelton, as if committing accounting fraud was just another day at the office — which to him it was, as would soon become all too clear.
Henry Silverman was predictably livid when Scott Forbes told him what had just transpired in Connecticut. He tried to contact Walter Forbes, but learned that that gentleman of leisure was on vacation in Hawaii and wasn’t receiving calls. Walter did eventually deign to send an email in response to the CEO’s increasingly furious queries, saying that they would get together and sort everything out when he came home in a few weeks. Like Shelton, he seemed to believe that the discovery of a $165 million shortfall was no big deal — or else he had made a strategic decision to act as if it was.
Not realizing that he would soon be wishing that $165 million was the full extent of the discrepancy in CUC’s books, Silverman said nothing publicly, hoping this could all still be swept under the rug as the mere teething problems that always accompany big mergers, even as he privately vowed to be rid of Walter Forbes by hook or by crook. “I can’t have people working with me that lie to me!” he raged.
Rather belying his own attempt to treat CUC’s accounting irregularities as No Big Deal, Walter Forbes, upon his return from Hawaii, refused to meet with Silverman at the headquarters of the company that they supposedly ran together. Instead he insisted that Silverman and his closest lieutenants talk with him and his on neutral ground, in a Manhattan hotel suite. This meeting took place on April 1, which must have struck Silverman as an appropriate date, seeing how Forbes had fooled him into merging their companies. Brushing off all of Forbes’s efforts at preliminary light conversation, Silverman got straight to the point — or rather to the ultimatum. He was prepared, he said, to look for a way to keep CUC’s shortfall from becoming public and placing Forbes in serious legal jeopardy. He would do this not for Forbes’s sake — for Forbes, he made it clear, he had nothing but contempt — but for that of Cendant’s employees and shareholders. As a condition, though, Forbes, Skelton, and the rest of the old CUC inner circle would have to open their books to him at long last — full transparency across the board. Then they would need to leave the company, just as soon as the necessary severance contracts and press releases could be crafted. According to most reports of the meeting, Forbes and his people agreed to this.
Having vented his rage on these eminently deserving targets, Silverman left the hotel suite feeling cautiously optimistic. The shortfall was ugly, but it shouldn’t be enough to sink the business as a whole. And the upshot of the whole affair was that he would get Walter Forbes and rest of the CUC amateurs out of his hair once and for all. Silverman ordered his accountants to conduct a thorough audit of CUC’s books, to provide him at last with that which he had been seeking for so long, the same thing that Ken Williams had sought much more lackadaisically before him: a proper picture of what exactly CUC did, how it did it, and where its money was coming from and going to. He gave them two weeks.
The day of reckoning was April 15, 1998. Silverman might have suspected the worst when he saw that his own people had brought two mid-level CUC accountants with them, and insisted that they give the presentation, as if afraid of becoming collateral damage of the CEO’s temper. Their fear was thoroughly understandable. For what was revealed on that day was a tale of fraud on a scale literally unprecedented in the history of American business. Over the past three years alone, CUC had conjured out of thin air more than half a billion dollars in revenue that had never actually existed in the real world. To Walter Forbes, business had been a shell game. Now you see it, now you don’t.
CUC’s long tradition of financial malfeasance had apparently begun, as these things so often do, with dubious short-term measures that were intended merely to grease the wheels of the company’s legitimate operations as they passed from a slow-moving present to a doubtless supersonic future. Already before the end of the 1980s, CUC had taken to booking pledged membership fees — fees that would be realized only if the members in question didn’t cancel, which they frequently did — as guaranteed revenues at the start of each fiscal year. More and more such schemes came into play as Walter Forbes and his cronies fell further and further down the slippery slope of fraud. When a new fiscal year began, they would figure out how much money they needed to have made during the last one to slightly outperform Wall Street’s expectations, then fiddle with the books appropriately. Jerry Bowerman of Sierra, in other words, had been onto something when he pointed out to Ken Williams how weirdly consistent CUC’s revenue growth had been for years and years. “That’s categorically impossible,” he had said. “Does not happen.”
Except, that is, in the case of fraud. The scope of the malfeasance was breathtaking, permeating every layer of the company, as later described by the forensic accountant Ron Rimkus.
According to later testimony by the company and the SEC, CUC managers would analyze the difference between actual financial results and the estimates put out by Wall Street analysts at the end of each quarter. They would then target specific aspects of the business to adjust in order to inflate earnings. After determining the best areas to change, the managers would then instruct others in the company hierarchy to adjust the various accounts — thus creating a false income statement and balance sheet. Their methods included under-funding reserves, accelerating recognition of revenues, deferring expenses, and drawing money from a merger account to boost income. After lower-level managers made the accounting changes to the financials, the cycle would be completed by adjusting the top line of quarterly changes and, subsequently, making back-dated journal entries at the division level to get the general ledger to balance. CUC’s leadership was able to hide the irregularities through misrepresented accounting entries, often moving certain transactions off the books. For a company of this size to maintain two sets of books requires a widespread internal effort to produce the second set of books so the company can present a blend of truth and fiction to the auditor without getting caught.
Eventually, CUC started to run out of internal revenue streams to which it could apply its portfolio of tricks. It was at this point that Walter Forbes began aggressively buying up other companies, among them Sierra On-Line and Davidson and Associates. These transactions were always conducted in stocks, never cash. The fraud that followed depended on the concept of the “merger reserve,” meaning the cash profits and assets that the acquired company brought with it into the new relationship. CUC reported this reserve as operating income for the parent company. In order to keep the hamster wheel spinning, of course, CUC had to keep buying more companies with the funny money it had “earned” from its last round of acquisitions. Underneath his unruffled exterior, Walter Forbes had been paddling as furiously as a duck on a placid pond.
But there had to come an end point, when neither the internal shenanigans nor the acquisitions could continue to paper over the discrepancy between the money CUC said it was making and the money it was really making. This limit point was looming by 1997. And this was what had set Walter Forbes down at a table with Henry Silverman, to negotiate a merger on a whole different scale from the acquisitions he had carried out to date. That said, it’s hard to identify what his real endgame in all of this actually was. He had to know that the fraud would come to light soon after the merger was consummated, and even he could hardly have been delusional enough to believe that Silverman would be willing and able to cover it up and let bygones be bygones. We can only conclude that chicanery had become such a way of life that the deal was worth it to him just to keep the wheel spinning for a few more months. When you get down to it, everything he and his people had done before negotiating the merger had been equally short-term. It was just a question of surviving and continuing to play the rich and successful businessman for today. Tomorrow could be dealt with when it came.
For once, even Henry Silverman was rendered speechless when he was told all of this about the man to whom he had shackled himself. After he picked his jaw up off the floor of his office, his analytical mind went to work. He knew right away that there could be no attempt to hide, minimize, or excuse this fraud; to do so would be to run the risk that the legal authorities would suspect that he and his people were also complicit in it in one way or another. The only way to save Cendant, and with it his own reputation, was to get out in front of the scandal before it broke on its own. He prepared a press release, to be sent out just after the markets closed on that very day. It spoke vaguely of “accounting irregularities” that had been perpetrated by “certain members of the former CUC management,” then announced matter-of-factly that the latter company’s earnings for 1997 would have to be adjusted — reduced, that is — by $165 million immediately, with more such adjustments very likely to come later. Having fired off this bombshell, Henry Silverman went home to get a good night’s sleep, knowing the storm that would break over his head when the next day’s trading began.
The tempest was as violent as he had anticipated, if not worse. Almost 110 million Cendant shares were traded that day, setting a Wall Street record. The stock price plunged from $36 to $19, reducing the company’s market cap by $14 billion. The first three shareholder lawsuits had already been filed before the trading day was over. In the weeks that followed, Cendant adjusted the figure of $165 million to $260 million in missing revenue for 1997 alone, with yet more years full of “irregularities” still craving investigation. Within six months, the stock price would be down to $9, the shareholder lawsuits numbering more than 70.
With characteristic brazenness, Walter Forbes contended that he had known nothing of the fraud committed on his watch — a claim of innocence that was, even if believed, as damning in its way as a confession, what with the degree of incompetence and negligence it would have to reveal. Nevertheless, forgetting what had been discussed in that Manhattan hotel suite on April 1, he fought to stay on as the current chairman of the board and the CEO in waiting of Cendant. He urged stonewalling opacity to the rest of the board as an alternative to Silverman’s strategy of transparency. The ruthless Wall Street money man thus found himself cast in the unwonted role of Cendant’s voice of conscience. “To urge me, as you seem to do, to not properly portray accurate information about our businesses,” wrote Silverman to Forbes in a letter (“I had difficulty looking at him” face to face, he admits), “appears to be of similar ilk to the conduct that brought us to this situation. I will not do that.”
Silverman didn’t manage to force Forbes out once and for all until July of 1998. When Forbes did leave, he took with him ten members of his board (good riddance, thought Silverman!) and a $47.5 million severance check. Whatever the long-term future held for Walter Forbes, he would have no problem continuing to enjoy his current lifestyle for the time being.
While Forbes was doing so, Henry Silverman rolled up his sleeves and set to work repairing the damage the disastrous merger had done to his own, legitimately profitable company. It was a daunting task, but it would prove not to be an impossible one. Hewing still to his strategy of powering through the heart of scandal so as to put it behind him as quickly as possible, Silverman agreed to shell out $2.83 billion in December of 1999 to settle the various shareholder lawsuits. The fact that Cendant, the name now associated with the biggest accounting scandal in American business history, was almost unknown to the American public in any other context, being hidden behind a welter of other brand names that they did know well, was an immeasurable aid to its survival; few consumers made any mental connection to the scandal when they booked a room at a Days Inn or rented a car from Avis. Indeed, most of those rental-car, hotel, and real-estate franchises which Cendant administered were still doing pretty darn well out there in the real world. For all of its difficulties, then, Cendant still had real money coming in, enough to offset the missing funny money of CUC over the long arc of time. It would survive and even expand its franchising reach well into the new millennium. In 2005, it voluntarily broke itself up into four separate companies to better service its increasingly diverse portfolio of brands. Henry Silverman, the first, last, and only CEO of Cendant, walked away from that culmination of fifteen years of work with a cool $250 million. Seen from this perspective, the CUC merger seemed like little more than a bump in the road.
As for Walter Forbes: the pace of criminal law for white-collar offenders like him is regrettably slow in the United States, but, in some cases at least, some form of justice is served in the end. After eight years of legal wrangling, he was convicted of conspiracy to defraud and two counts of submitting false reports to the Securities and Exchange Commission in October of 2006. (E. Kirk Shelton had been found guilty of a similar collection of charges a year earlier.) Forbes was sentenced to twelve years in prison and $3.28 billion in fines and restitution — fines which, needless to say, nobody expected him to ever be able to pay. By the time he was released from prison in July of 2018, the financial scandal that had made him and CUC infamous for a while had been all but forgotten, eclipsed by even bigger ones like the collapse of Enron and the machinations of Bernie Madoff. As far as I know, he is still alive today. If you asked the current 82-year-old Walter Forbes about his history, and if he happened to be in an honest mood when you did so, perhaps he would tell you that his halcyon decades as a jet-setting titan of industry were worth the twelve years of his life he had had to spend in prison to pay for them. He booked his revenue well ahead of his debt to society, just the way CUC always did it.
The infamous merger between CUC and HFS was actually a brilliant stroke of luck for the former Sierra On-line. For if that deal hadn’t gone through, CUC would almost certainly have crashed and burned at some point during late 1997 or early 1998, with no Henry Silverman to hand to clean up the mess. Blizzard Entertainment was doing so well by then that someone would probably have found a way to scoop it out of the wreckage, but Sierra, which could boast of no similar run of recent hits — Ken Williams’s parting gift to his old company of Half-Life wouldn’t be released until November of 1998 — might very well have been permanently buried under the rubble.
As it was, Silverman had no long-term interest in maintaining the software arm of Cendant. For him, games studios and publishers were a distraction from Cendant’s core business, to be unloaded as quickly as possible. To accomplish this, he replaced the rather clueless Chris McLeod — yet another legacy of Walter Forbes whom he couldn’t be rid of fast enough — with a well-respected games-industry executive named David Grenewetzki, whose last job had been with the publisher Accolade. While Blizzard was obviously doing just fine as it was, Grenewetzki’s brief when it came to Sierra and the rest of the software arm was to trim the fat, to finish and ship whatever was reasonably far along and worth the effort, and to cancel whatever was not, all in order to make this superfluous part of Cendant look as attractive as possible to potential buyers. If he did a good enough job that a buyer wanted to keep him on afterward, more power to him.
By this point, King’s Quest: Mask of Eternity had been dawdling along without any firm sense of direction for some eighteen months. Grenewetzki ordered Roberta Williams, Mark Siebert, and the rest of their unruly crew to kick it into gear and get the game done in time for Christmas, assigning them a new set of minders to settle their disputes and make sure they met their milestones. These were effective enough: the game shipped on November 24, 1998. Roberta Williams was largely missing in action during the last few months, choosing to join her husband on a vacation to France while the rest of the team was crunching.
Playing the game today puts me in mind of Douglas Adams’s description of an aye-aye lemur: “a very strange-looking creature that seems to have been assembled from bits of other animals.” Or perhaps the old joke about a camel being a horse that was designed by a committee is more apropos. Collaboration, feedback, and testing are of incalculable importance in any kind of game development, mind you; in fact, I would argue that one of the biggest problems with virtually all of Roberta Williams’s earlier games was that she didn’t engage in enough of these things. Yet a game also needs to have a firm sense of its own identity, which usually translates into having a decisive final arbiter in charge of it. Mask of Eternity all too clearly didn’t have that; neither Roberta nor anyone else was allowed to fill that role. In the absence of an empowered lead designer, Mask of Eternity became a game of bits, a collection of disparate parts that clash more often than they gel.
This strange-looking digital creature that was assembled from bits of other popular games sports the acrobatic challenges of Tomb Raider, the ultra-violent action of DOOM and Quake, the CRPG-lite trappings of Diablo, and even from time to time the puzzle-solving of a traditional King’s Quest, all of it implemented more or less badly. The floating camera is an especial pain, requiring constant fiddly adjustments that break up whatever sense of flow the rest of the game permits you to establish. The writing veers all over the place, from Roberta Williams’s trademark fairy-tale whimsy to adolescent gross-out humor that wouldn’t have felt out of place in Duke Nukem 3D. The dialog is delivered for some reason in a pseudo-Shakespearian diction, all “thee” and “thou” and “by your leave, milady,” read by dulcet-toned British voice actors who clearly have no idea what the characters they’re playing are on about and don’t much care. The game is very hard to connect with King’s Quest at all for long periods, until someone seems suddenly to remember the name on the box and throws in a few gratuitous references to King Grahame’s earlier adventures or the history of Castle Daventry. I’m not the best person to wax outraged over all the ways that Mask of Eternity betrays its lineage, given that I’m the farthest thing from a hardcore fan of King’s Quest in general. Yet even I can see why so many gamers who are much more invested in the series than I am consider this, its final official entry prior to a brief-lived and almost equally underwhelming 2015 revival, such an insult to everything that came before.
As is the case with so many such Frankenstein’s monsters, it’s hard to figure out just whom Mask of Eternity was supposed to be for. The series’s usual pool of players — who tended to skew younger and to include more women and girls than was the norm even for the adventure genre in general — would be put off the first time they punched a monster in the face and saw its head fly off in a shower of blood and gore. And yet the demographic that enjoyed more violent and visceral games would be equally put off by the harsh reality that Mask of Eternity just wasn’t a very good action game long before they came across the first convoluted adventure-style puzzle to cement their indifference. You can’t be all things to all people — especially not with all-around execution as poor as this.
If anything, reviewers were kinder to the game than it deserved. Computer Gaming World magazine gave it four out of five stars, whilst admitting that it “required an open mind” and that “the old-school puzzles may frustrate newbies, while the veterans may be annoyed at the jumping and the combat.”1 The website GameSpot called it “enjoyable” but “occasionally maddening”: “Sierra should be applauded for trying something new, even if its reach somewhat exceeds its grasp.”
But gamers weren’t buying such prevarications, and didn’t buy many copies of Mask of Eternity. Its commercial failure killed the longest-running series in the adventure genre as dead as one of its pixelated goblins. It marked the final nail in the coffin as well of Roberta Williams’s tenure as the “Queen of Adventure Games.” She wouldn’t design another game for a quarter of a century. The times, they were a-changing.

Sierra’s decision to drop the Roman numeral from the eighth King’s Quest game is indicative of the confused, have-your-cake-and-eat-it-too quality of all of its messaging around Mask of Eternity. The logic was that the new generation of gamers Sierra was hoping to attract would be intimidated by its being the eighth game in a series, might even feel they shouldn’t bother with it if they hadn’t played the previous seven. But then, if you are so concerned about reaching these people, why call it a King’s Quest game at all? The only cachet that brand might have held for most of them was the negative cachet of the “kiddie games” their moms or sisters used to play.
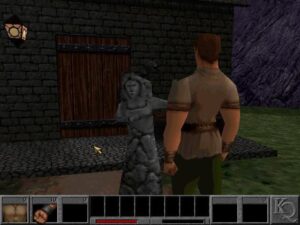
Mask of Eternity’s hero Connor looks like he could break Sir Grahame or any of the other protagonists from the first seven King’s Quest games in two without straining his tree-trunk-sized arms.
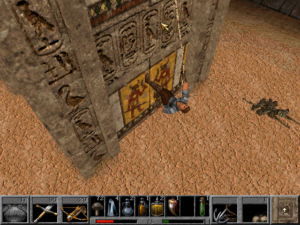
This level — err, area — is Egyptian-themed. What does this have to do with King’s Quest? Beats me… but Stargate SG-1 was popular on television at the time. Got to tick those boxes…
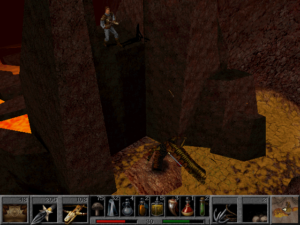
“Oh, great, another jumping challenge! I love those, especially with these extra clunky controls!” said no player of Mask of Eternity ever.
Did you enjoy this article? If so, please think about pitching in to help me make many more like it. You can pledge any amount you like.
Sources: The books Not All Fairy Tales Have Happy Endings: The Rise and Fall of Sierra On-Line by Ken Williams, Financial Shenanigans: How to Detect Accounting Gimmicks & Fraud in Financial Reports by Howard Schilit, Stay Awhile and Listen, Book II: Heaven, Hell, and Secret Cow Levels by David L. Craddock, Gamers at Work: Stories Behind the Games People Play by Morgan Ramsay, and Last Chance to See by Douglas Adams and Mark Carwardine. Wired of November 1997; New York Times of May 27 1997, July 4 1998, July 5 1998, and June 16 2000; Wall Street Journal of July 29 1998; Fortune of November 1998; Next Generation of June 1997; Sierra’s customer magazine InterAction of Fall 1996, Holiday 1996, and Fall 1997; Computer Gaming World of April 1999.
Online sources include “How Sierra was Captured, Then Killed, by a Massive Accounting Fraud” by Duncan Fyfe at Vice, Ron Rimkus’s analysis of the CUC/Cendant debacle for the CFA Institute, “A Pathological Probe of a Pool of Pervasive Perversion” by Abraham J. Briloff of Baruch College, Forbes’s report of Walter Forbes’s sentencing, and the vintage GameSpot review of King’s Quest: Mask of Eternity.
I also made use of the materials held in the Sierra archive at the Strong Museum of Play.
Where to Get It: King’s Quest: Mask of Eternity is available as a digital purchase at GOG.com, packaged together with the more fondly remembered King’s Quest VII: The Princeless Bride.